What is Fill Rate?
Fill rate refers to the percentage of customer orders fulfilled on time without stockouts, helping businesses assess order fulfilment, demand satisfaction, and guide manufacturing and procurement strategies. Understanding the fill rate meaning is essential for evaluating how effectively a business can meet customer demand and manage inventory. High fill rate measures are vital supply chain KPIs that signal efficiency in supply chain operations and support strong customer service outcomes.
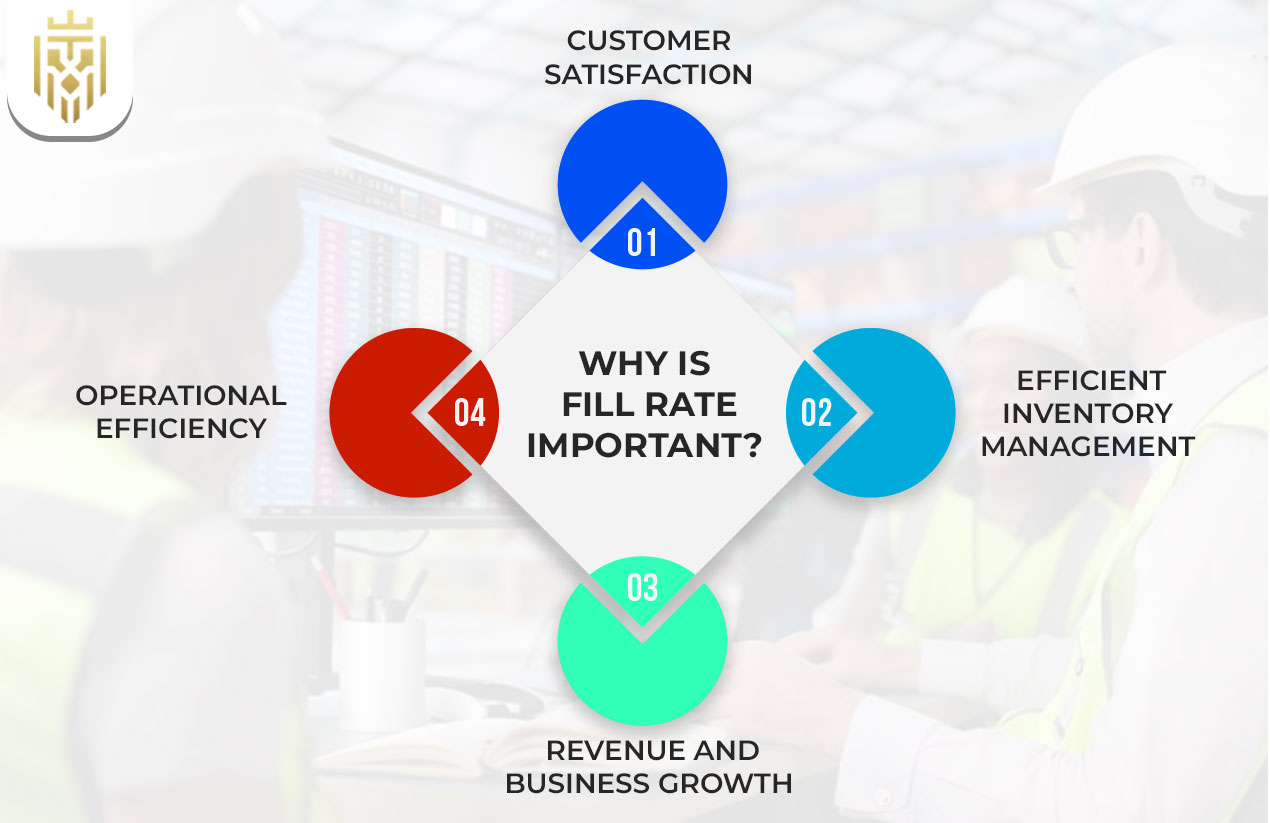
Why is Fill Rate Important?
Fill rate is crucial for customer satisfaction, inventory management, operational efficiency, and revenue growth, directly influencing customer loyalty and business profitability. A high order fulfilment rate ensures that businesses excel in meeting customer demand, which in turn boosts their competitive edge. It also enhances service level performance within the supply chain, contributing to better logistics flow and fewer supply chain disruptions.
-
Customer Satisfaction
A high fill rate plays a key role in customer satisfaction, as it reflects a business’s ability to fulfil orders accurately and promptly. This reduces delays and stockouts, reinforcing trust and loyalty while enhancing the overall customer experience through reliable service. It supports higher service level standards and helps maintain a 100 fill rate, especially when integrated with a robust warehouse management system.
-
Efficient Inventory Management
A high fill rate demonstrates effective inventory management, showing a company’s ability to meet demand without delays. It minimises stockouts, enhances customer satisfaction, and helps reduce operational costs. These factors together can positively impact profitability and increase overall business efficiency. Effective inventory optimization strategies and real-time updates from an inventory management system further strengthen fill rate performance
-
Revenue and Business Growth
Maintaining a high fill rate supports business growth by preventing lost sales due to stockouts or backorders. Reliable order fulfilment fosters customer trust and encourages repeat purchases, ultimately boosting revenue and enabling long-term growth for the business. High fill rate contributes to better order fulfilment efficiency, ensuring inventory levels are aligned with total customer orders.
-
Operational Efficiency
A high fill rate boosts operational efficiency by reducing backorders, improving inventory accuracy, and streamlining order fulfilment. It helps maintain smoother processes across departments, enhances customer experience, and supports better alignment between supply chain operations and customer expectations. It also reflects positively on warehouse management and helps monitor unit fill rate consistency.
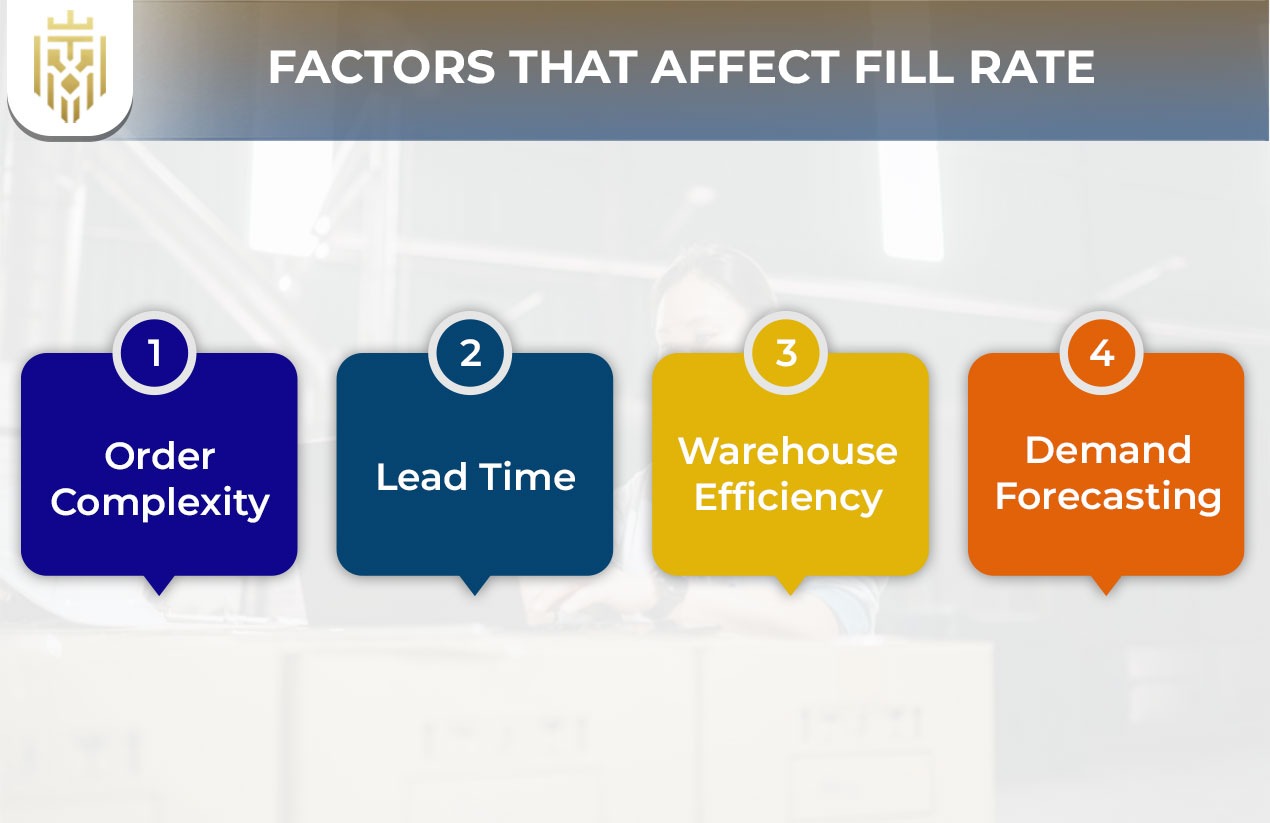
Factors that affect Fill Rate
Factors affecting fill rate include order complexity, longer lead times, and warehouse efficiency. These elements influence how quickly and accurately businesses can process and fulfil customer orders, significantly impacting overall supply chain performance and service level expectations across the board.
-
Order Complexity
Orders with multiple items, customizations, or special packaging requirements can lower the fill rate, as these factors increase processing time and handling effort. This complexity can delay shipments and affect accuracy, thereby hindering a business’s ability to meet customer demand effectively. It also leads to low fill rate outcomes if not managed efficiently through logistics and inventory fill rate tracking.
-
Lead Time
Longer lead times due to factors like supplier delays or shipping distances reduce the fill rate by delaying order fulfilment, which can lead to stockouts and backorders. This inefficiency poses a significant challenge in consistently meeting customer demand. Businesses must address such delays using agile supply chain methods and monitor rate measures to maintain service consistency.
Warehouse Efficiency
Warehouse efficiency directly impacts fill rate; faster picking, packing, and shipping processes improve order fulfilment. Inefficient warehouse operations can lead to delays and errors, resulting in a reduced fill rate that ultimately affects customer satisfaction and a company’s ability to meet customer demand. Using a modern warehouse management system and aligning processes with supply chain management goals helps resolve this.
Demand Forecasting:
Fill rate impacts demand forecasting precision; a higher fill rate may indicate overstocking risks, while a lower rate could signal stockouts. Companies can fine-tune inventory levels based on these insights to meet customer demand effectively. Incorporating fill rate into supply chain KPIs ensures better visibility and decision-making across the supply chain.
Types Of Fill Rate
Fill rate types include order fill rate, warehouse fill rate, case fill rate, vendor fill rate, line fill rate, supplier fill rate, and inventory fill rate, each offering insights into different aspects of order fulfilment, inventory management, and supplier performance. Tracking each helps improve logistics coordination and boosts service level reliability.

-
Order Fill Rate
Order fill rate measures the percentage of customer orders fulfilled without stockouts or backorders, indicating how efficiently a company meets customer demand. A high order fill rate enhances overall customer satisfaction. It is also a primary indicator of supply chain responsiveness and improves order fulfilment efficiency.
-
Warehouse Fill Rate
Warehouse fill rate measures the percentage of orders shipped from a warehouse out of the total received, evaluating warehouse performance in fulfilling orders efficiently and accurately. It is critical for inventory management, ensuring that stock levels are maintained appropriately and achieving a high fill rate is essential for meeting customer expectations in logistics.
-
Case Fill Rate
Case fill rate tracks the percentage of product cases shipped compared to the total ordered, commonly used by distributors in bulk industries like food and beverage. This metric ensures efficient large-scale order fulfilment and supports a high fill rate, allowing companies to manage excess inventory while maintaining a steady supply chain.
-
Vendor Fill Rate
Vendor fill rate measures the percentage of vendors able to fulfil their order shipments on time, reflecting their ability to meet contractual obligations. This metric provides insights into supplier reliability and overall supply chain performance, which is crucial for optimising procurement strategies and avoiding supply chain disruptions.
-
Line Fill Rate
Line fill rate tracks the percentage of individual order line items fulfilled out of the total items ordered. This helps businesses identify gaps in product availability or inefficiencies in fulfilling multi-item customer orders, which is vital for maintaining a high fill rate and ensuring that each SKU meets sku fill rate standards.

-
Supplier Fill Rate
Supplier fill rate measures the accuracy and timeliness with which suppliers fulfil orders. It is crucial for evaluating supplier performance, helping businesses identify reliability issues and maintain smooth operations through timely and accurate deliveries of required inventory. This is a cornerstone of effective supply chain management and successful logistics execution.
-
Inventory Fill Rate
Inventory fill rate reflects the percentage of customer orders fulfilled immediately from existing stock. It is calculated by dividing shipped orders by total orders and multiplying by 100. A high rate signals strong inventory management practices and the ability to meet demand with available inventory consistently.
How To Calculate Fill Rate?
Fill rate is calculated as (Total orders shipped / Total orders placed) x 100, indicating the speed and reliability of a company’s order fulfilment process. Understanding the fill rate formula helps businesses measure their effectiveness in meeting customer demand consistently and can serve as a benchmark among rate measures within the supply chain.
-
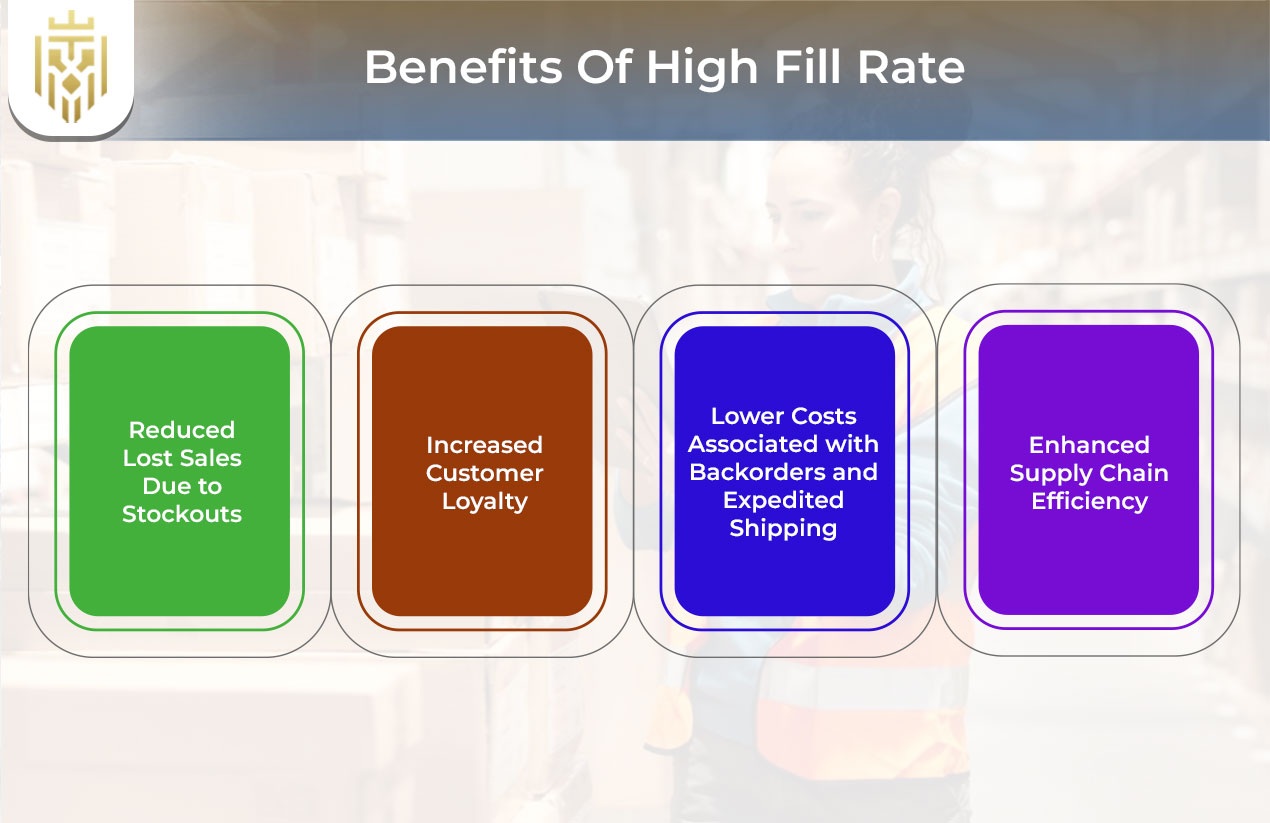
Benefits Of High Fill Rate
A high fill rate ensures timely and complete order fulfilment, reducing stockouts, boosting customer satisfaction, lowering operational costs, and enhancing supply chain efficiency. It directly supports sales growth, service level improvements, and overall business performance while reducing the impact of low fill rate challenges.
-
Reduced Lost Sales Due to Stockouts
High fill rates ensure that most orders are fulfilled completely and on time, reducing the risk of stockouts. This prevents lost sales opportunities and keeps customers from turning to competitors due to unavailability of products they need. Proper monitoring of fulfillment rate metrics can further reduce gaps in the supply chain.
-
Increased Customer Loyalty
When customers consistently receive complete and timely orders, their trust in the company increases. A high fill rate strengthens this relationship, leading to repeat purchases and increased customer loyalty, which is vital for long-term business sustainability. High service level performance and marketing mix alignment further drive loyalty and brand preference.
-
Lower Costs Associated with Backorders and Expedited Shipping
A high fill rate reduces reliance on costly measures like backorders and expedited shipping. By fulfilling orders from current stock, businesses lower operational expenses and avoid inefficiencies linked to emergency restocking. Accurate inventory fill rate data can help in this supply chain cost control.
-
Enhanced Supply Chain Efficiency
A strong fill rate indicates a reliable and well-functioning supply chain. It reflects accurate demand forecasting, efficient processes, and responsive inventory systems, which collectively lead to better customer service, cost savings, and improved overall logistics and service level performance.
FAQs
1) What is Fill Rate?
Fill rate is the percentage of customer orders fulfilled on time without stockouts, indicating a business’s efficiency in meeting customer demand and managing inventory effectively.
2) Why Fill Rate is Important?
Fill rate is crucial for customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and revenue growth, directly influencing customer loyalty and overall business profitability by ensuring timely order fulfillment.
3) What are the Types Of Fill Rate?
Types of fill rate include order fill rate, warehouse fill rate, case fill rate, vendor fill rate, and line fill rate, each assessing different aspects of order fulfilment and inventory management.
4) How to Calculate Fill Rate?
Fill rate is calculated using the formula: (Total orders shipped / Total orders placed) x 100, reflecting a company’s order fulfilment speed and reliability in meeting customer demand.









