The Difference between 3PL and 4PL:
3PL (Third Party Logistics) basically deals with the management of the physical flow of goods from one location to another. In contrast, 4PL (fourth-party logistics) themselves consolidate and coordinate the supply chain process; they may work with one or more 3PLs and also provide the management of the solution with strategic direction.
What is 3PL?
Third-party logistics or 3PL is the contracting of logistics functions to others, which comprises transportation management, warehousing, order picking, inventory control, and other related services including freight forwarding. In other words, it enables companies to outsource specific activities to third parties capable of managing them more efficiently, thus freeing up time to concentrate on areas of corporate competency.
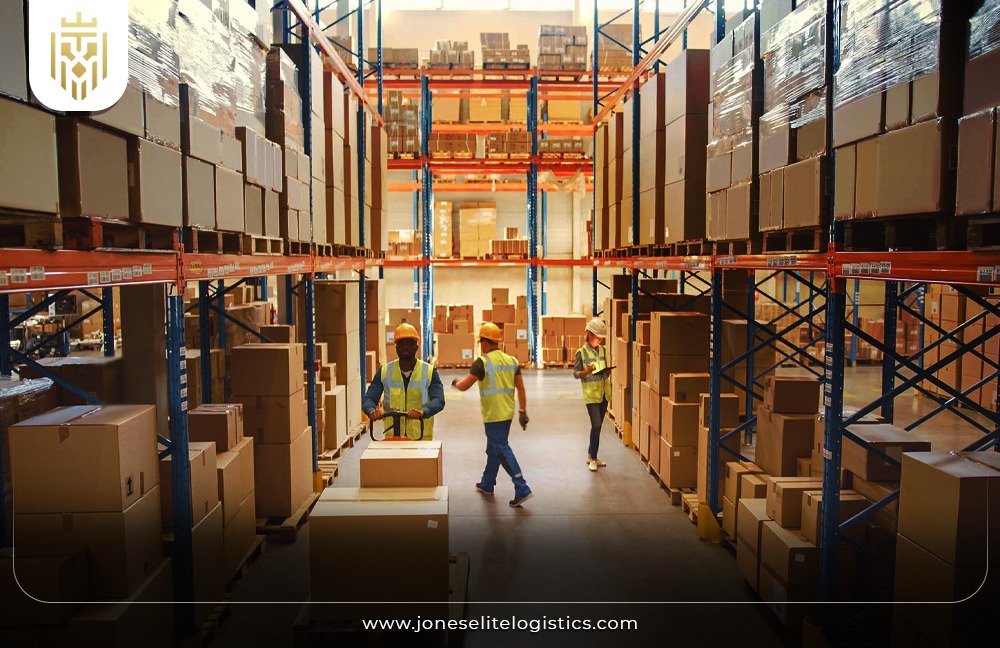

How does 3PL work?
3PL providers act as outsourcing partners that manage specific parts or all aspects of logistics processes. This enables firms to leverage specialized logistic capacities with the additional advantage of not having to invest in fixed structures and human resources.
Receiving:
In the receiving process, 3PL providers take products from suppliers, inspect them in terms of accuracy and quality, and record them in the inventory systems. It is important to track stock with a view to ensuring that the supply chain is smooth.
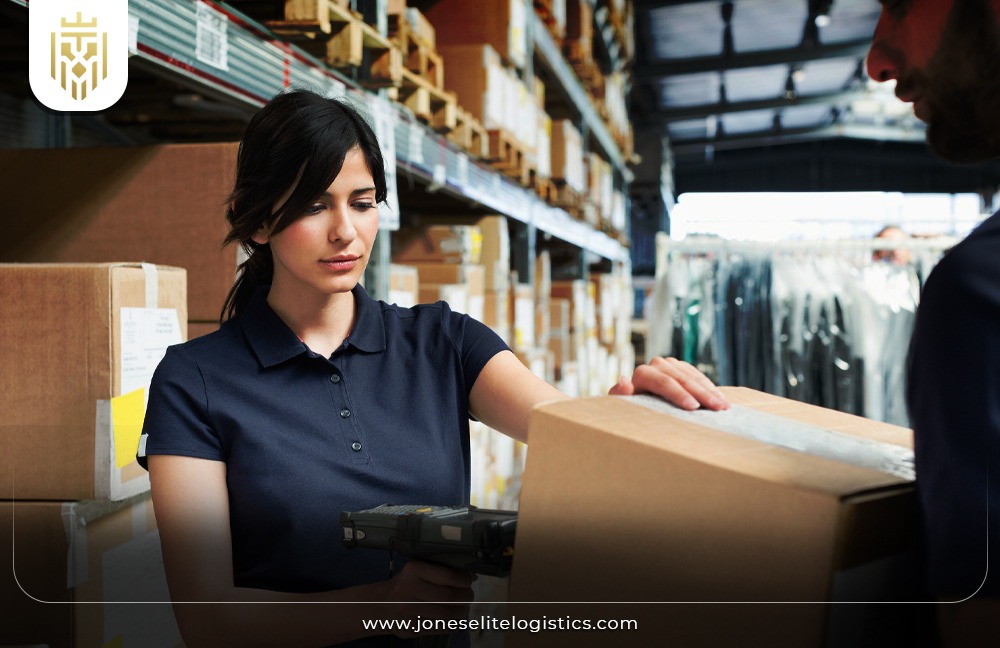

Warehousing:
One of the main services offered by 3PL providers is warehousing with facilities for storage of inventory. 3PL providers also ensure the purposeful management of warehousing space to manage inventory effectively and support the order pick-up process. They make sure that products are made available on time and at the same time make sure that the cost of storage is kept low by using proper technologies.

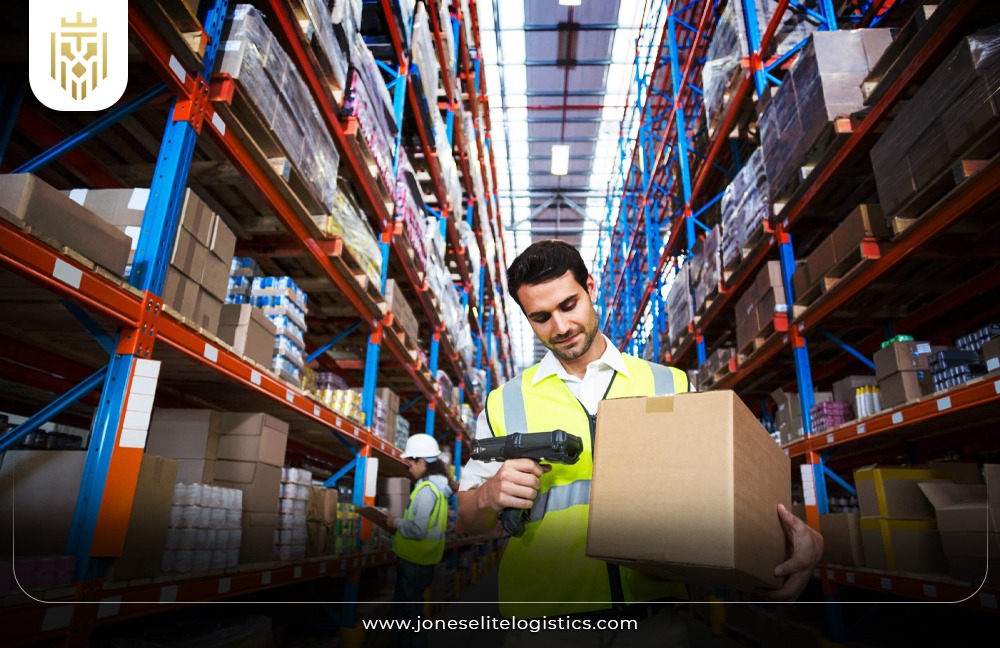
Picking:
Picking is the process where the items are taken out of the stock in order to satisfy the demand of the customers. 3PL providers use multiple picking methods which include batch picking, zone picking, or wave picking with the aim of reducing the time taken to process an order. In picking process and use of up-to-date tracking information technology, they are able to create optimal picking processes that meet customers’ expectations of delivery.

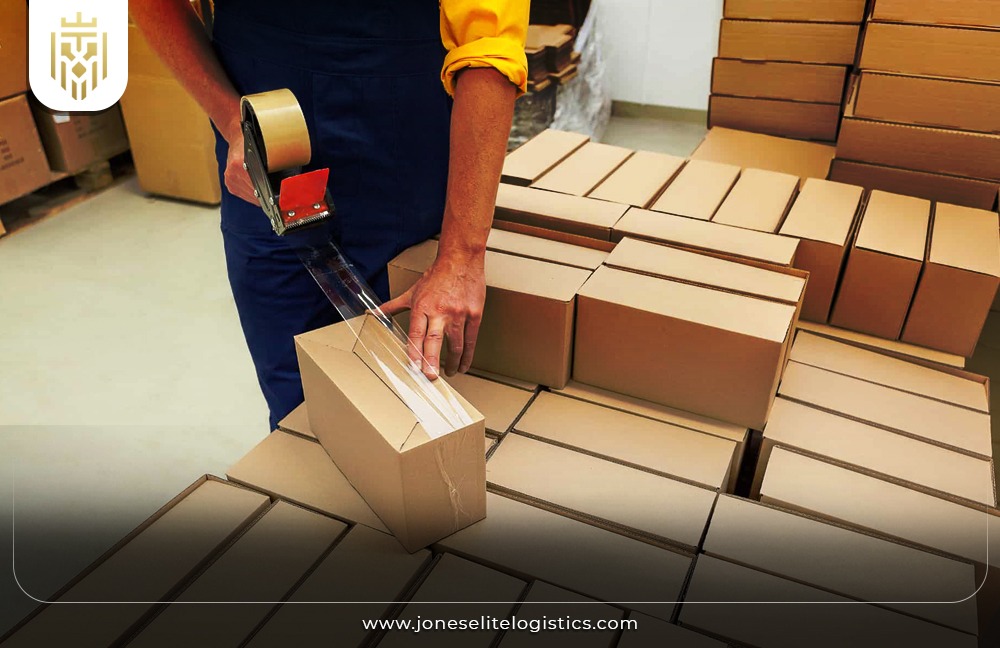
Packing:
Packing entails placing the orders in a shipper’s format encasing the products in a way that will protect the item as the consumer wishes it were. Based on the literature review 3PL providers use packaging auxiliaries and methods that protect products in transit while it reduces the size and weight of the packing container to reduce transport costs. Their strategies and approaches to packing impact the organizational operations and customers by improving packing efficiency.
 Shipping:
Shipping:
Transportation is a key element in the supply chain that logistics Third third-party logistics (3PL) firms cover as they involve the movement of products from the depot to the final consumer. They exploit control over the network of carriers, secure shipping rates better than other channel members, and choose the most appropriate mode of transport to deliver goods on time at the least transport cost. By efficient shipping logistics, they can plan and coordinate delivery routes about their actual shipment tracking.
Returns:
Return management is another aspect of logistics management that most third-party logistics firms participate in. They develop efficient logistics management practices for handling returned products, checking the returned items with any form of defect or damage, and putting the items back on the shelves as soon as possible. That way, through the best practices of reverse logistics management, they promote higher customer satisfaction levels and control the negative effects of returns.
Role of 3PL in Supply Chain management:
3PL is a critical link in the supply chain because it offers strategic skills, tools, and mainframes dedicated to supporting the management of logistics functions. Outsourcing logistic functions to third-party providers frees the concerned business from having to bear certain responsibilities and will derive certain benefits such as lower overhead costs, increased overall productivity, and also flexibility. In addition, 3PL providers provide companies with flexibility in that the providers can expand as necessary in response to more actual and/or anticipated demand
What is a 4PL:
A 4PL or Fourth Party Logistics Provider, is a logistics integrator who takes full responsibility for the client’s supply chain and arranges all the logistics processes. While 3PL is centered on processing the physical movement of goods, 4PL involves a higher level view by managing a range of 3PLs and other supply chain members.

How does 4PL work?
4PL providers are clients’ main facades and are responsible for coordinating all logistics processes starting from the planning phase to direct implementation. They identify supply chain needs, contract and administrate suitable 3PL providers, and further drive improvements to the processes involved for increased efficiency and adaptability.
Transportation:
4PL providers sought to provide optimal transport channels, and involve carrier selection and choice of mode of transport. They plan and schedule all consignments, monitor delivery, and specialize in dealing with constraints to achieve delivery on time and at reasonable transportation costs.

Warehousing:
It controls the warehousing by assessing the necessary volume for storage, positioning the storage locations, and providing orders related to inventory. They optimize the storage area of the warehouse determine the pattern of materials received and issued to users accurately update records of stored items.

Inventory Management:
4PL employs sophisticated systems for controlling inventories for the purpose of making sure it is stocked to the right levels and reducing instances of stock out while containing overhead costs. They use demand forecasting, order inventory, and inventory distribution plans, and put all three into practice.
Shipping :
4PL has the responsibility of organizing shipping operations and the transport of the goods from the providers to distribution points and end-users. They choose the right conveyance mediums, bargain the freight costs, and track the shipment delivery to address the concern for timely and efficient delivery to the consumers.
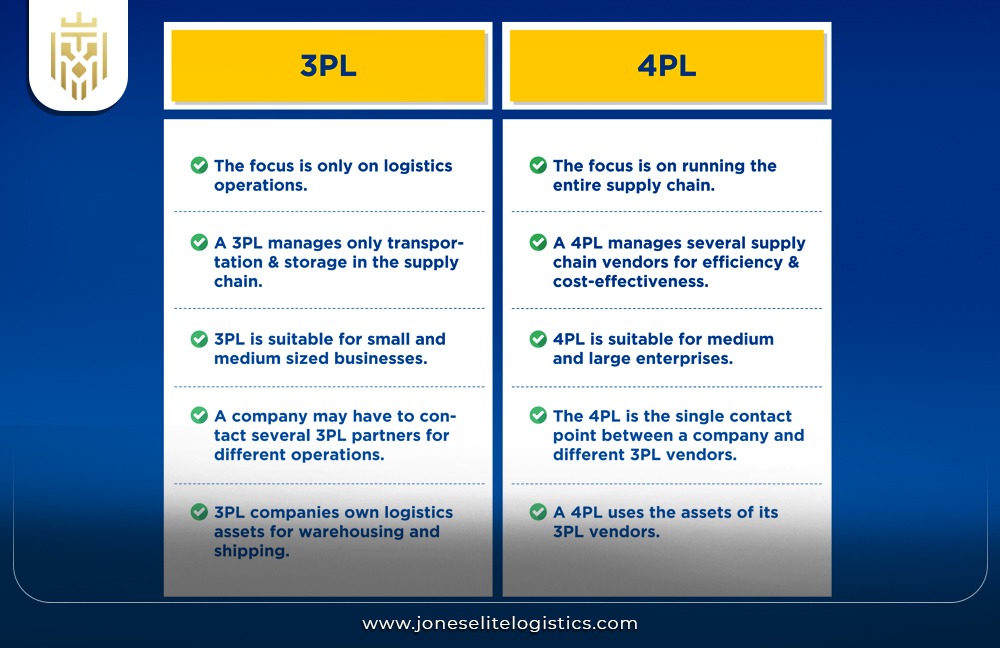
Key Differences between 3PL and 4PL:
A core difference lies in their scope: 3PL deals with the physical supply chain, while 4PL is responsible for supervising multiple 3PL providers in an ideal efficient chain of supply.
Focus & Functionality:
While 3PL is mainly involved with operations of a physical nature, 4PL is a strategic partner that manages and drives the entire concept of supply chain integration, fully in charge of centralizing and synchronizing all the logistics to create optimum value.
Cost Reduction:
Compared to 3PL, 4PL often delivers higher potential cost savings through efficiency gains made possible through scope consolidation, more effective network design, and the use of sophisticated tools and techniques to minimize costs.
Organizational Structure:
While 3PL providers are independent organizations, 4PL works more closely with the client as it may even employ resources that are part of the client’s organization to ensure they directly see how the services given by the provider are positioning the organization vis-à-vis its business strategies.
Coordination of service providers:
4PL as a concept also takes up the timely organization of and cooperation with other supply chain members such as 3PL, carriers, suppliers, or anyone who is directly or indirectly connected with the client requirements in supporting the overall Integrated Supply Chain.
Technology and Integration:
4PL has to develop a better forecasting mechanism for things like demand, inventory, and risks by integrating technology solutions with the real-time supply chain network that works in conjunction with several parties.

Client Interaction and Communication:
4PL provides clients with status reports, performance data, and advisory information on a frequent basis to ensure effective teamwork and organizational development are on the right track and are in sync with business objectives and frameworks.
How does a 4PL differ from 3PL:
4PL is also a source of supply chain management solutions that are more tactical than 3PL goods that are logistically oriented. 4PL logistics operates by pulling together and overseeing multiple 3PL providers with diverse capabilities; on the other hand, 3PL logistics specializes in only transportation, storage, or distribution.
Which is better for your business: 3PL v/s 4PL?
The major difference between 3PL and 4PL lies in the fact that while 4PL takes up a more strategic role in supply chain management, 3PL performs a solely functional role. 3PL is applicable for those companies which need outsourcing solutions for certain logistics services while 4PL would better suit those for who the provider has to be a strategic planner and coordinate supply chain management. Make sure to weigh your business requirements, the costs of acquiring and implementing the chosen option, as well as further business development strategy to select the most effective logistics option.
FAQs
1) What is the difference between 3PL and 4PL?
3PL is involved in the handling of individual logistics activities, while 4PL is holistic in its approach to coordinating various activities optimally.
2) What is 3PL?
3PL or outsourcing of logistics functions proves to be efficient and effective as it reduces complexities and enhances service quality by outsourcing with outside professionals and resources.
3) How does a 3PL work?
3PL providers take charge of operations from the receipt of goods up to and including return management; this frees up more of the business’s operational time for strategic and more essential functions.
4) What is 4PL?
4PL is a solution advisor, analyzing play requirements, providing play management of service providers, and playing an active role in implementing performance improvement technology.
5 ) How does a 4PL work?
4PL entails the centralization of multiple logistics providers where the providers in the system use technology to foster communication and make decisions aimed at enhancing performance in supply chain management.









