What Makes Operations Truly Efficient?
Real operational effectiveness involves matching resources, processes, and individuals to well-defined purposes with the least amount of waste. Companies that know what is operational efficiency all about concentrate on providing as much output as possible with the least input possible so that it is sustainable and flexible and can be measured with increasing performance in all functions without compromising business quality or consistency in services.
Why Streamlined Workflows Transform Outcomes?
Automatic workflows eliminate redundant processes, saving time and reducing mistakes. They increase efficiency of operations by defining roles, eliminating bottlenecks and facilitating speedy decision-making. The outcome is more effective working relationships, predictable performance, and the ability to provide consistent customer value, even in high-demand or fast-changing business conditions.
The Ripple Effect of Efficiency Throughout Teams
Teams flourish when processes are visible and resources are well-distinguishable. Efficiency is contagious – it improves productivity and communication and minimises stress. By improving operational efficiency and effectiveness, leaders enable individuals to have a sense of ownership, which translates to improvement in problem-solving and overall performance across departments.
Proven Tactics to Level Up Efficiency

To enhance efficiency in business through operations, there should be a focused effort to change– the identification of gaps, the elimination of redundancies, and the introduction of best practices. Depending on the use of technology or the redesign of processes, every tactic should be associated with your objectives so that you can not only achieve deadlines but also ensure similar quality standards in different operational conditions.
Map & Trim Inefficient Steps
Workflow mapping assists in identifying inefficiencies before they can impair outcomes. Companies can enhance operational efficiency synonyms such as productivity, agility, and consistency by cutting redundant processes. This approach will minimise delays and enhance handovers and make every work directly contribute to business goals without wasting essential time and resources.
Lean Workflow Techniques
Lean principles are aimed at removing waste and maximising value creation. They are particularly useful in manufacturing, where any additional motion, overproduction or idle capacity can damage profitability. The lean strategy will make operational processes valuable, transparent, and constantly optimised according to changing customer and market needs.
Automate Repetitive Tasks
Automation minimises the human touch and liberates teams to do more valuable work. Organisations can apply their understanding of ‘enhance operational efficiency’ meaning to achieve faster completion, fewer errors, and more homogeneous results, through automation of repetitive processes. It is also a technology-orientated solution that can generate scalability so that businesses can respond without the need to scale up labour costs proportionally.
Set Smart Metrics
Intelligent measurements quantify significant progress, not irrelevant action. The emphasis on actionable KPIs allows a team to be aligned with strategic objectives, and the removal of non-value-adding activities keeps operations lean and performance outcomes uniform across various performance cycles or operating environments.
Track Real-Time Performance Signals
Leaders can address underperformance and capitalise on improvement opportunities by performing real-time monitoring. This is a proactive initiative that helps in improving operational efficiency in business through freeing of resources when the need arises, high productivity, and the ability to provide quick reaction to market or internal changes in business operations.
Empower Teams Culture
Innovation is encouraged when employee suggestions are invited to make improvements. With a culture of shared ownership, the operational challenges are resolved quickly, processes evolve with minimal interruption, and efficiency becomes a shared mission, not a top-down directive.
Lean Six Sigma to Cut Variation
Lean Six Sigma is a combination of waste minimisation and the elimination of defects. Through these means, firms can upgrade their efficiency of operations as well as ensure uniformity in quality. The emphasis on data-driven problem solving also serves to streamline work processes and realise consistent, high-value output across projects or production runs.
Track Progress Using Clear Metrics
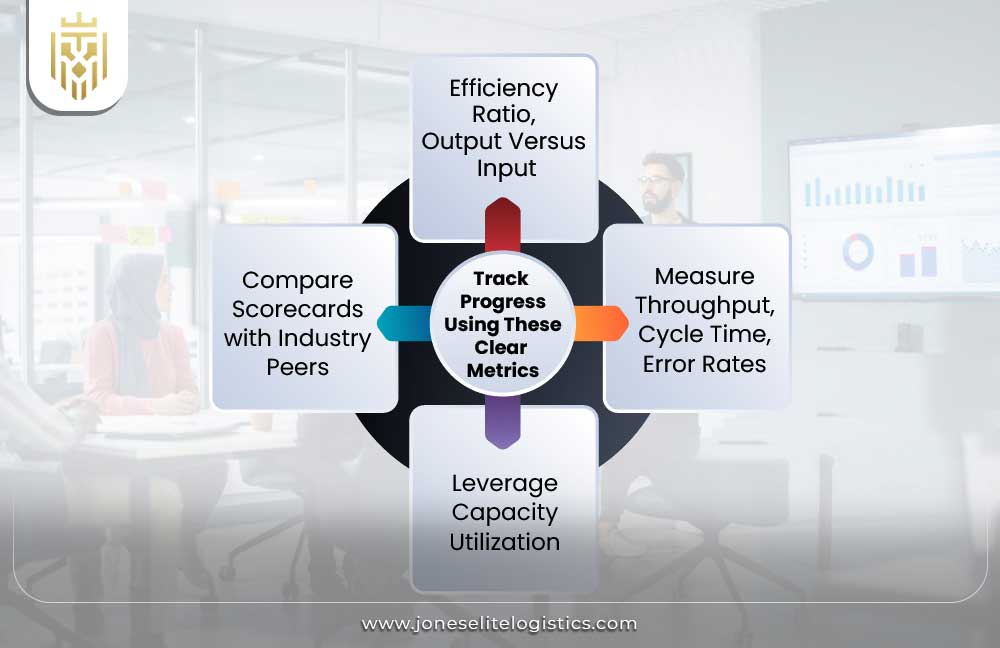
Monitoring would be needed to guarantee the long-term success of operations. Through consistent measuring of outputs, inputs, and wastes, the leaders are in a position to improve operational effectiveness and efficiency, with all the dips in performance detected promptly and the necessary adjustments made in ways that accommodate both short-term requirements and long-term strategic goals.
Efficiency Ratio—Output Versus Input
This indicator helps assess the effectiveness of resources in terms of their outcomes. Knowing this ratio facilitates the definition of what is operational efficiency in practice: creating more with less without sacrificing quality or overworking teams, and knowing when and how to invest in tools, training, and process improvements.
Measure Throughput, Cycle Time, Error Rates
Throughput indicates capacity, cycle time indicates speed, and quality is measured by error rates. This combined high level of monitoring keeps operations balanced and fast enough to keep up with demand and ensures high standards of output consistency and reliability throughout all functions.
Leverage Capacity Utilization
Capacity utilisation indicates the use of resources to the maximum or underutilisation. An effective rate is a good sign, whereas too high or too low is a warning of a possible problem with planning, staffing, or workload that should be corrected before affecting delivery schedules.
Peer Scorecard Comparison
Comparisons to industry peers point out gaps and opportunities. When competitors are consistently better than you in one particular measure, it could be best practices that you can borrow to reduce performance lag and stay competitive within your segment of the market.
Results of Improving Operation Efficiency

Business outcomes are measured in efficiencies gained, faster delivery, lower costs, improved margins, and happier teams. To leaders, the outcomes also mean that leaders are better positioned in the market, are more adaptable, and create more confidence amongst stakeholders regarding long-term operational capabilities.
Quicker Turnaround and Fewer Slip-Ups
Effective workflows provide a significant minimisation of delays and errors. This aptly contributes to improving operational efficiency in manufacturing and services alike, as scheduled completion of predictable work and no-defect work on time leads to the creation of customer confidence and its ability to enable competitive pricing without margin erosion.
Cost Savings and Stronger Margin Control
Cost savings are achieved by reducing waste and rework and increasing productivity. Companies that improve operational efficiency and effectiveness retain a stronger control over margins, thereby enabling them to invest savings in innovation, staff training, or strategic market growth.
Adaptability in Fast-Moving Environments
Efficient processes in organisations allow them to change direction more rapidly when markets move. This flexibility guarantees sustainability in the face of supply-chain delays, regulatory shifts, or sudden changes in demand, keeping them ahead of more rigid competitors.
Elevated Team Morale and Ownership
Employee stress levels decline and engagement increases when operations are running smoothly. It makes teams feel more in control and proud of what they do and want to keep high standards, producing a positive feedback loop in productivity and satisfaction.
FAQs
1) What does operational efficiency mean for businesses?
Operational efficiency refers to the high level of output at the lowest rate of resources being wasted. It concentrates on workflow optimisation, cost reduction, and quality consistency, allowing businesses to stay competitive, flexible, and sustainable in the long term.
2) How can small companies start improving without big budgets?
Small businesses can optimise by doing process mapping, reducing redundancy, automating repetitive work, and implementing lean practices. Culture and low-cost digital tools are a quality priority, which can aid productivity without causing burdensome investments.
3) What are the best metrics to monitor operational performance?
Key metrics are throughput, cycle time, error rates, and capacity utilisation. Observing these indicators allows companies to trace their efficiency and maintain the balance between the speed and quality of their work, and align operational goals with those of the market.
4) How do organizations sustain efficiency in the long run?
Organisations maintain efficiency through continuous improvement, team ownership, employee training, and flexibility in workflows harnessed by real-time data insights, which make them resilient, agile, and consistent in changing business conditions.