The cold chain system was established in the 1960s-70s for the sole purpose of maintaining cold-chain temperatures for vaccines, which would allow the eradication of smallpox and expansion of immunisation. Key advancements in cold chain maintenance of vaccines include freeze-dried vaccines, refrigeration devices, temperature monitoring, and specialized vaccine carriers. These innovations allowed the vaccines to be distributed while maintaining their potency and efficacy.
Cold Chain in Vaccine Distribution:
Cold chain systems are implemented to ensure temperature-sensitive vaccines, which need to have stringent conditions of storage, are kept at the correct cold chain vaccine temperature for maintaining potency during storage and distribution processes. Well-equipped refrigeration and rigorous protocols, along with trained personnel, will avoid wastage and make immunisation possible. Strong preservation of vaccines through the cold chain will keep public health safe by ensuring that vaccines are efficacious during movement and storage.
Why do Vaccines have to Be Kept Cool?
Vaccines are susceptible to fluctuations in temperature, which have an adverse effect on their active ingredients and can be magnified by poor management of cold chain vaccine temperature. A proper cold chain maintenance of vaccines gives temperature stability, which prevents loss of potency, thus ensuring effectiveness. A cold chain system makes use of specialized refrigeration and insulated containers in protecting the vaccines from heat exposure in their distributions.

Vaccine Storage Temperature:
Heat exposure might damage the biological components of a vaccine, making it incapable of stimulating a proper immune response. An appropriate cold chain vaccine temperature maintenance is a prerequisite for ensuring vaccine effectiveness. A well-managed cold chain system conserves the integrity of vaccines-from production to administration-thus reducing spoilage risk.
Standards for Vaccine Storage and Transportation:
Most vaccines require cold chain storage of vaccines between temperatures of 2°C and 8°C to maintain efficacy. Cold chain maintenance of vaccines ensures that this temperature range is preserved from the time of manufacturing to administration. Improper storage-whether too hot or too cold-can do irreversible damage to immunogenic potency, thus reducing efficacy.
Real-Time Monitoring:
Real-time monitoring is needed, thus requiring constant readings within the cold chain vaccine temperature range. The vaccine storage conditions are being continuously monitored by different sensor systems, while data logging serves to record trends for later analysis. Alerts notify health institutions of deviations, ensuring timely intervention to prevent both damage and wastage of the vaccines.
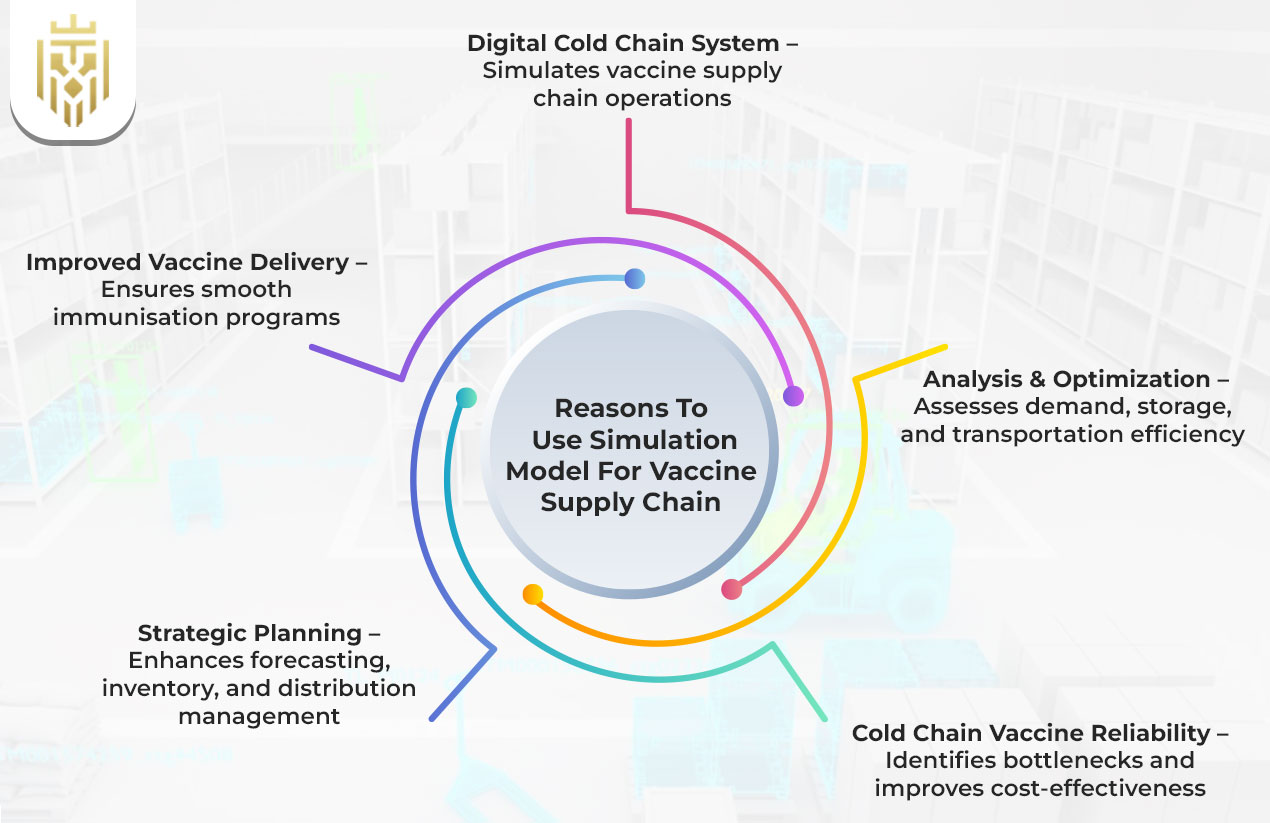
Why Use a Simulation Model for a Vaccine Supply Chain?
A simulation model replicates the cold chain system digitally. It analyses demand patterns, vaccine storage, and transportation efficiency along with cold chain vaccine reliability. It provides support for demand forecasting, inventory management, and distribution planning while identifying bottlenecks and making cost use more effective. Hence, this promotes the efficiency of vaccine delivery and also ensures a smooth immunisation program.

What happens if the cold chain breaks in vaccine distribution:
In case of failure of the cold chain system, vaccines lose potency because of insufficient cold chain vaccine temperatures, which make them ineffective. Thus, vaccine wastage, the occurrence of diseases, and monetary losses increase. So strict monitoring, emergency protocols, and cold chain maintenance of vaccines can be able to avoid such conditions and preserve vaccine integrity.
HHow to maintain a cold chain of vaccines?
Maintaining proper cold chain conditions for vaccines means protecting vaccines by refrigeration at 2-8 °C while using an array of monitoring systems to measure temperature changes, avoiding exposure to light, and preventing freezing. A stringent set of procedures is to be followed during vaccine handling by trained personnel; they must also regularly inspect the vaccines to preserve the proper cold chain condition as their integrity. Proper storage of vaccines with respect to cold chain maintains their potency; thus, minimising losses and improving actual immunisation outcomes.
Recent Innovations in Vaccine Cold Chain:
Recent developments in the cold chain include drone deliveries for remote areas; thermostable storage that reduces temperature dependence of cold chain vaccines; and needle-free vaccine patches that simplify distribution. These improvements increase cold chain maintenance of vaccines, thereby guaranteeing a wider immunisation coverage. Strengthening vaccine storage and transport through such innovations creates efficiencies and makes access easier, particularly in areas with limited infrastructure.
Conclusion
A well-managed cold chain will ensure that vaccines are stored in the range of temperatures where they still have potency and effectiveness. Developments in cold chain storage, monitoring, and distribution of vaccines are now aiming at making access easier, reducing wastage, and using immunizations as leverage for hard-to-reach or underdeveloped areas to ensure even better public health protection.
FAQs
1.What is Cold Chain Vaccine?
Cold chain systems are implemented to ensure temperature-sensitive vaccines, which need to have stringent conditions of storage, are kept at the correct cold chain vaccine temperature for maintaining potency during storage and distribution processes. They need to be stored at temperatures between 2°C-8°C which are the most commonly used ranges, to ensure efficacy.
2.Why Use a Simulation Model for a Vaccine Supply Chain?
A simulation model is used for digitally replicating the cold chain vaccine logistics, analysing the temperature range within the setup, demand, storage, and distribution efficiencies. It optimises vaccine storage and prevents interruptions in cold chain maintenance of vaccines that offers effective immunisation strategies.
3.What happens if the cold chain breaks in vaccine distribution?
A break in the cold chain system exposes vaccines in the unlink between two points to a temperature other than that which is normally maintained from the storage facility of cold chain vaccine to the distribution site. Furthermore, this ban in the cold chain introduces wastage, disease outbreaks, and losses from financial costs to the health ministries. This justifies the reason for real-time monitoring and maintenance of the cold chain for vaccines.









