What are Supply Chain Metrics?
Supply chain metrics are various performance, efficiency, and reliability indicators of the supply chain operations of a particular company. They basically check the management of the flow of goods, information, and finances from the source to the end customers.
They help organisations identify areas of improvement, streamline processes, and reduce operational costs. For instance, metrics like the percentage of deliveries made on time, the time taken for the life cycle of an object, and inventory turnover provide an important insight into the efficiency of the supply chain concerning business objectives. In essence, supply chain analytics turn everyday operations into measurable data that can be acted upon.
Importance of Supply Chain Metrics

Tracking supply chain metrics is essential for achieving operational excellence and maintaining competitiveness in today’s fast-moving markets. They not only help in evaluating efficiency but also align supply chain performance with broader business objectives.
Decision Making
Accurate data generated from supply chain metrics enhance sound day-to-day decision-making. Managers identify inefficiencies, accurately gauge demand, and deploy resources to uphold service levels. This responds well to sudden changes in the market and creates an uninterrupted flow of operations within the organisation.
Performance Tracking
Metrics help organisations to track the performance of their activities continuously. This monitoring is against agreed standards and benchmarks. The tracking of such fields as delivery fulfilment, production lead times, and supplier delivery assists in the early discovery of any performance gaps so that remedial actions can be taken without delay.
Customer Focus
Efficiency in the supply chain is directly related to customer satisfaction. Improvements in customer acceptance outcomes, delivery time, product accuracy, and responsiveness are output factors that enhance customer relationships and brand image. Service levels and delivery accuracy are metrics that provide insight into how well customer expectations are being met.
Strategic Alignment
Good metrics translate between how well a business is working operationally and its strategy. When operations of a company and their supply chain goals—be they cost reduction, faster order fulfilment, and the like are integrated with strategic goals, this would assure sustainability, growth, and long-term success.
Important Metrics Used to Measure Supply Chain Performance
A well-designed supply chain performance framework uses multiple metrics to evaluate key stages from procurement and production to delivery and customer service. Below are some of the most significant ones.
On-time Delivery
This metric is used to measure the percent of deliveries arriving within promised delivery times. Always high on-time delivery rates represent the most effective logistics system, while lower rates would rather suggest the poor planning or delays generated by transport.
Cycle Time
Cycle time stands for how long it takes for some operations to be completed, such as an order being fulfilled or stock replenished. Shorter cycle times imply greater responsiveness and agility, thus providing a competitive strength for firms to counter fluctuating consumer demands.
Service Rate
The service rate measures the extent to which a company fulfils its customers’ requirements without any stockouts or delays in delivery. Higher service rates enable a really good inventory control as well as efficient synchronization of the supply chain.
In-full Delivery
This check determines the number of orders that went to customers in full without any missing items. It is a crucial measure that reflects operational efficiency and order accuracy, reducing the potential for re-delivery or customer complaints.
Order Accuracy
This metric measures the degree to which delivered orders follow customer instructions. Higher accuracy excludes the factor of returning and lowers operational cost, thus increasing customer satisfaction and trust levels.
Inventory Turn over
Inventory turnover indicates how often a stock is sold and replaced during a given time period. The higher the turnover rate, the better the inventory management, while a lower rate means that there is overstocking or slow sales.
What are KPIs?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are strategic measurements that track progress toward specific business objectives. Metrics traditionally provide operational data while KPIs deal with those results that impact the success of an organisation.
With regard to supply chains, KPIs create a linkage between day-to-day performances and major objectives like profitability, sustainability, and customer satisfaction. They make sure the business never veers from what actually matters and continuously improves through hard results.
KPIs in Supply Chain
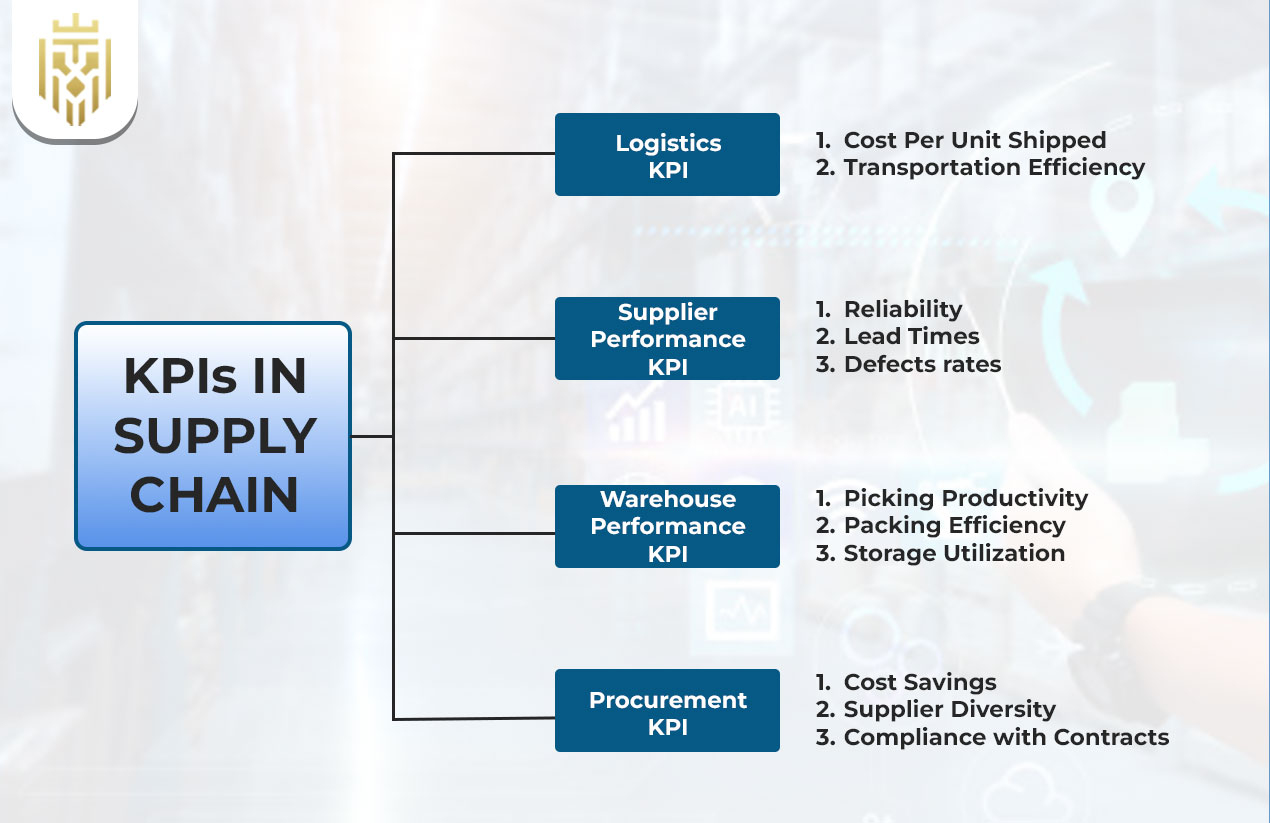
Supply chain KPIs are categorised based on their function across logistics, supplier management, warehousing, and procurement. Each category focuses on a specific aspect of supply chain effectiveness.
Logistics KPI
These KPIs assess the efficiency of transportation and distribution processes that move goods across the supply chain.
Cost Per Unit Shipped
This KPI represents a ratio of total logistics cost to the number of units shipped. It helps to reveal opportunities to save costs and make sure transportation expenses are in line with the stated profitability targets.
Transportation Efficiency
Transportation efficiency refers to the performance of transport operations as judged by criteria such as route optimization, load utilization, and timeliness of delivery. Thus, high efficiency would translate into reduced fuel consumption and speedier shipments.
Supplier Performance KPI
These indicators measure supplier reliability, consistency, and overall contribution to the supply chain’s performance.
Reliability
This KPI measures the extent to which suppliers are consistent in maintaining agreed-upon timelines and criteria. The effectiveness of reliable suppliers results in smooth workflows with few interruptions.
Lead Times
Lead time covers all times from placing an order to actually receiving the goods. Short lead times allow for quick replenishment and make production cycles more responsive.
Defects rates
Defect rate shows the percentage of products received with quality problems. Tracking this KPI will ensure that suppliers uphold product standards and continue to reduce wastage.
Warehouse Performance KPI
Warehouse KPIs track operational efficiency, space management, and workforce productivity within storage facilities.
Picking Productivity
With an increased number of orders or goods gotten for every hour of work by the staff, it places actual emphasis on productivity with efficient layout, streamlined processes, and proper training of the workforce.
Packing Efficiency
Packing efficiency considers the time taken and accuracy with which goods are packed for shipment. Packing efficiently reduces the risk of damage, lowers cost, and enhances client experience.
Storage Utilization
This KPI checks the adequacy provided for warehouse operations. Best utilisation will avoid unnecessary expansion and maintain the flow of organised inventory.
Procurement KPI
Procurement KPIs evaluate the effectiveness of purchasing strategies, cost management, and supplier relations.
Cost Savings
Negotiations, strategic sourcing, or improvement of processes in procurement should be tracked to measure cost savings.
Supplier Diversity
This measures what proportion of procurement is conducted with diverse suppliers. Having such a diverse supplier base strengthens resilience and supports innovation.
Compliance with Contracts
Trustworthy suppliers comply with the agreed terms and conditions, price, and service levels. In fair compliance, there is less room for dispute and more scope for open partnerships.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between supply chain metrics and supply chain KPIs
Metrics measure operational activities on a day-to-day basis, whereas KPIs focus on strategic objectives concerning an outcome for a business. KPIs usually aggregate several metrics into one measurable objective.
2. Can supply chain metrics improve collaboration with suppliers?
Yes. The sharing of performance data builds transparency and a culture of accountability; hence suppliers get clear about expectations and partnering to improve outcomes.
3. How do global disruptions affect supply chain KPIs?
Disruptions – Pandemic, war, and natural disasters – increase lead times, threaten transportation, and push up costs. Measuring KPIs in these times help companies strengthen their supply chains.
4. Why is benchmarking crucial in supply chain performance measurement?
Benchmarking evaluates company performance in comparison to that of the industry or competitor standards, identifying the good, the bad, and the opportunities for improvement.










