What is Hyperlocal Delivery?
Hyperlocal delivery is a logistical system in which goods are delivered from local merchants to customers residing nearby within a short time, generally on the same day or possibly within hours. It focuses on an extremely tight geographic area of just a few kilometres to provide prompt and efficient service. In cities across India, where convenience and speed matter, hyperlocal delivery has become a quintessential mode of everyday logistics for food, groceries, medicines, and other urgent items.
What is the difference between hyperlocal delivery and last-mile Delivery?
Hyperlocal delivery is a subset of last-mile delivery. While last-mile delivery marks the final leg from the distribution centre to the customer, hyperlocal delivery specifically stands in for the local sellers to local buyers. By virtue of its proximity and speed, last-mile delivery may extend farther distances and involve a more complex upside.
Features of the Hyperlocal Delivery Model
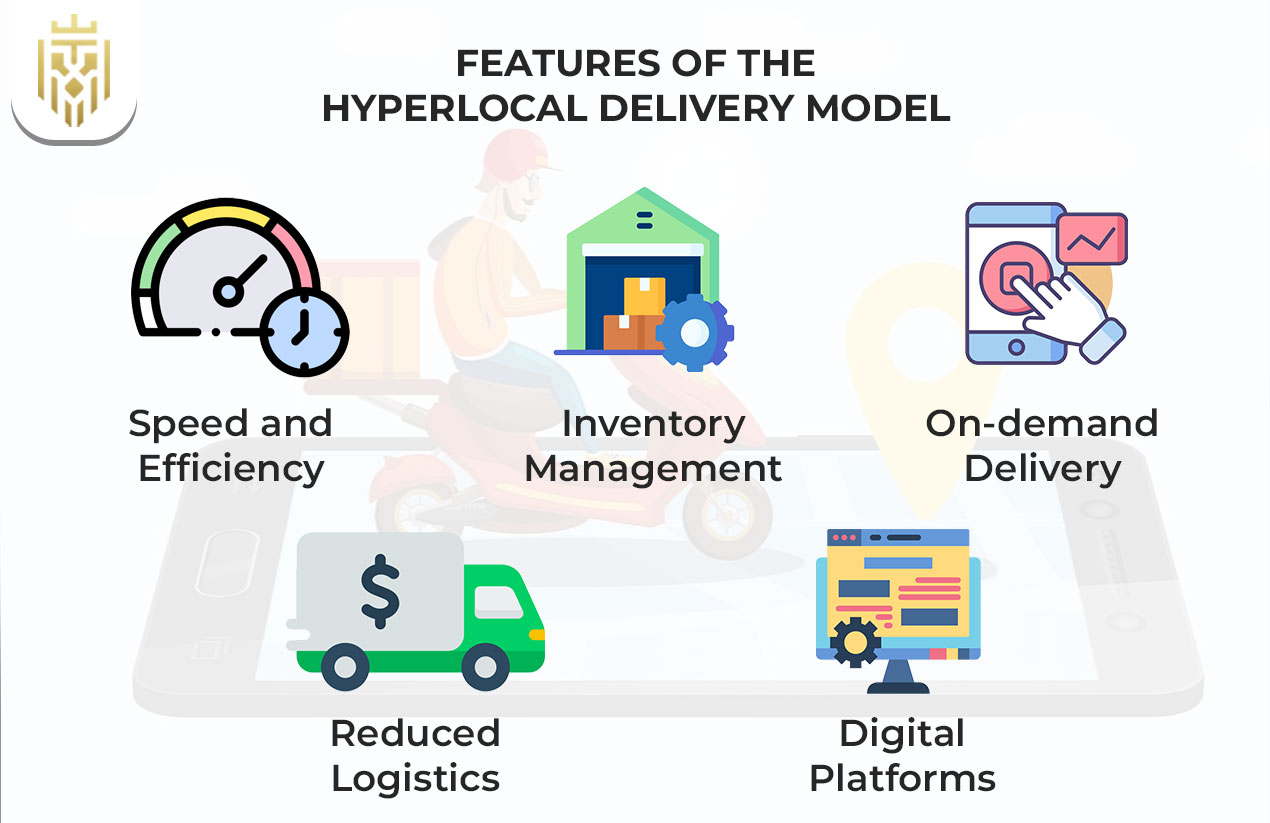
The hyperlocal model comes with specific traits that set it apart from conventional delivery services. These features drive its appeal among fast-moving, urban markets.
Speed and Efficiency
The deliveries take a matter of hours, so it’s very suitable for urgent or immediate orders like that of food, medicine, and other daily essentials. The speed ensures that businesses stand shoulder-to-shoulder with customer expectations in areas where convenience and immediacy take precedence.
Inventory Management
Real-time inventory updates help sellers manage stock levels and avoid cancellations due to stock unavailability. It also provides advantages for promotion and stock rotation while minimising chances for under stocking due to unexpected selling.
On-demand Delivery
This means the orders are picked and delivered immediately, as XYZ is the customer demand for instant gratification. This real-time fulfilment builds customer loyalty and encourages the repetition of purchases.
Reduced Logistics
Working within a reduced radius of delivery removes the need for huge warehouses and complex logistics setup. This gives the company an opportunity for leaner infrastructural setup and lower operational costs.
Digital Platforms
Running digital platforms through mobile apps or on the web is the main activity linking buyers, sellers, and delivery partners seamlessly. These platforms also allow for automated dispatching, route optimisation, and performance tracking.
How does the Hyperlocal delivery model work?
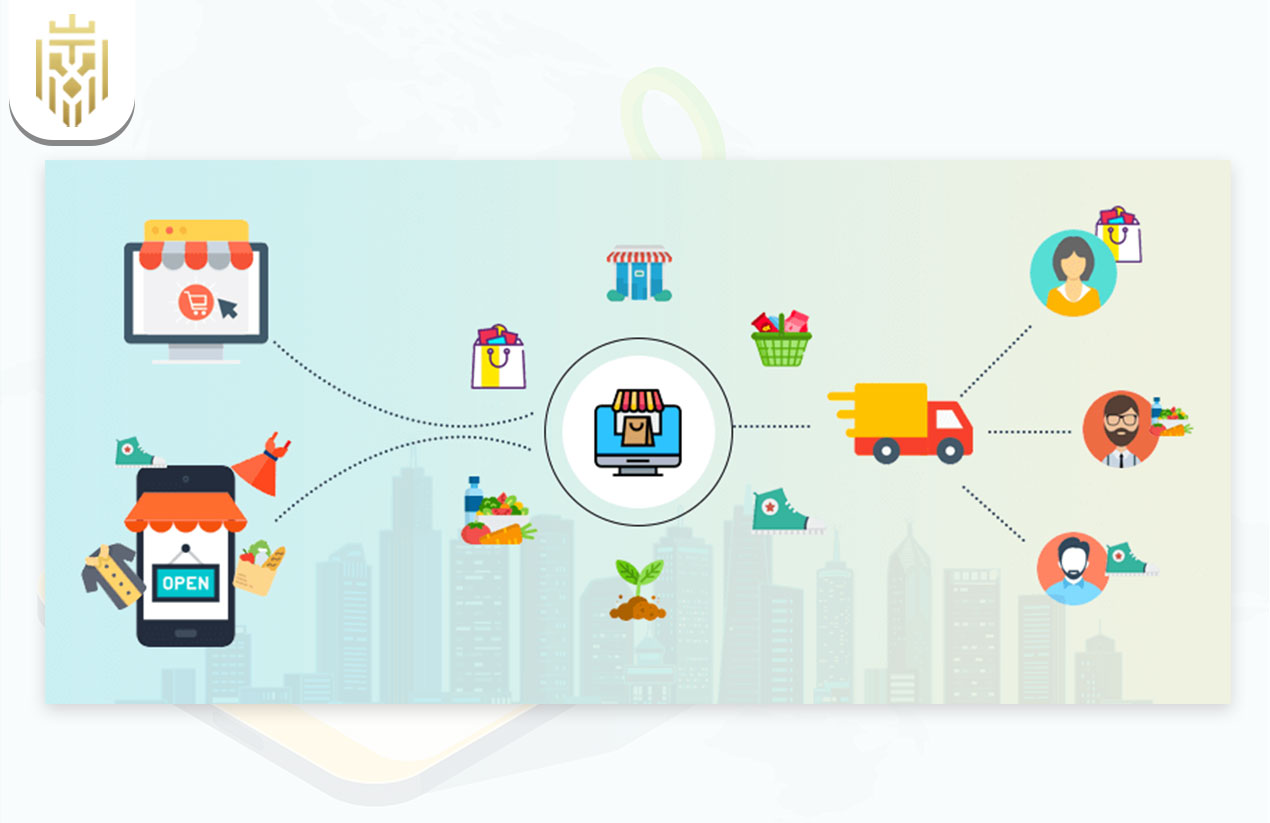
Being hyperlocal means that a customer places an order using an app or a website. The system then checks with sellers nearby and assigns the order to a local delivery partner. The goods get picked up and delivered directly to the consumer, often less than an hour later. Technology in fact plays an essential role in harmonising various stages of order placing up to delivery, ensuring that all proceedings are well-monitored and updated in real time.
Which type of businesses can choose a hyperlocal delivery model?
This model suits businesses dealing in everyday or urgent products. It helps local retailers and shops compete with top suppliers in providing prompt and reliable delivery. Groceries, beauty care, gifting, and home-cooked food fare best with this model due to their local demand and quick turnaround time.
Types of Hyperlocal Delivery
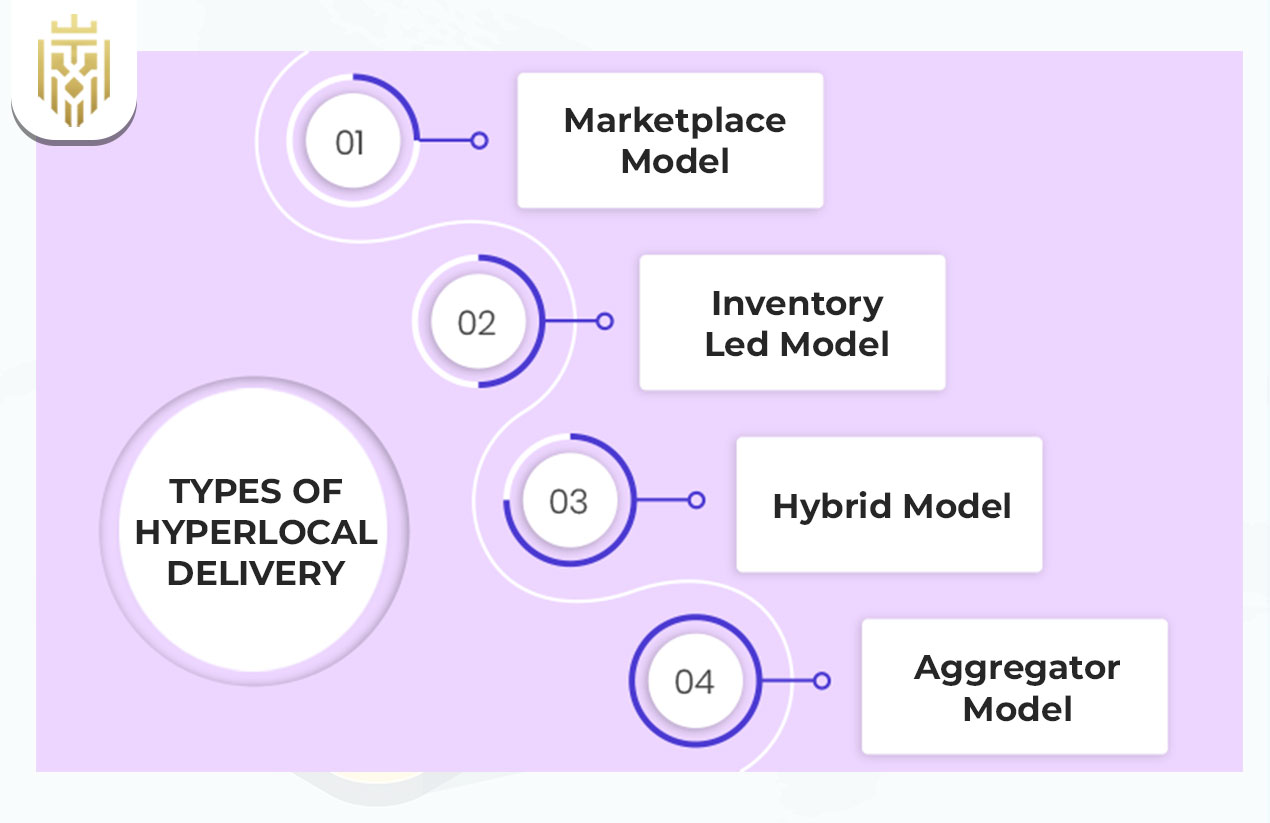
Hyperlocal operations can be structured in different ways depending on the business size and strategy.
Marketplace Model
Local sellers list products on a shared platform. Delivery management rests fully with the platform. This gives sellers visibility and access to customers without the need for logistics.
Inventory Led Model
The business either stocks its own inventory or delivers on behalf of someone else, to exert control over stock and service quality. The route is most narrow towards product consistency and brand standards.
Hybrid Model
Marketplace listing with limited inventory control for more flexibility and reach. This model balances the efficiency of centralised stock with the agility of decentralised fulfilment.
Aggregator Model
Third-party aggregators are hired to provide delivery partners, do their own logistics; yet they neither own the inventory nor the store fronts. It is the scaling solution for restaurants or retailers as they try to open up their delivery zones quickly.
Challenges of Hyperlocal Delivery
Despite its advantages, hyperlocal delivery presents several operational and strategic challenges that businesses must address.
Inefficient Order Clubbing
Sometimes, smaller orders that come from the same area are considered separate orders for delivery, creating more costs and lowering delivery efficiency; more fuel and time are consumed in doing so.
Poor Management of Non-Delivery Reasons
Reasons for failed deliveries, such as the customer not being available or incorrect addresses, are at times not noted or acted upon in any way. An order is affected in terms of reliability and cost tracking due to such invisibility.
Growing Cases of Fake Delivery Attempts
At times, delivery personnel may attempt to tarnish the image of the business by unfairly deeming an order undelivered or returned, thereby affecting business in terms of inventory records and operational costs.
Inaccurate Pickup ETA s
Pickup time estimation delays can lead to late deliveries and customer grievances. Repeat orders may also get affected owing to constant discrepancies in timing.
FAQs
1. What is Hyperlocal Delivery?
Hyperlocal Delivery is moving goods from a nearby seller to a nearby customer within a stipulated short time, usually on the same day.
2. What are the Features of the Hyperlocal Delivery Model?
Key features include real-time inventory, fast service, digital platforms, limited until the least logistics requirements, and on-demand fulfilment.
3. How does the Hyperlocal delivery model work?
Customers place order online; local sellers pick up orders and venders-deliver directly, whereas digital tracking and coordination services support local vendors all along.
4. What are the Challenges of Hyperlocal Delivery?
To name a few, an inefficient grouping of orders, handling of failed deliveries, delivery fraud, and erroneous pickup time estimates.









