What is Finished Goods Inventory?
Finished goods inventory includes products fully manufactured and ready for sale to vendors, retailers, and consumers. It plays a vital role in tracking production and ensuring financial accuracy for accurate asset valuation. A finished goods inventory example could involve rural electric cooperatives tracking manufactured items like transformers, poles, or wiring that are ready for distribution to meet rural energy demands. Although these goods are finalized, they may serve as raw materials in another business’s inventory process, demonstrating inventory’s fluid role in supply chains.
Importance of Finished Goods Inventory:
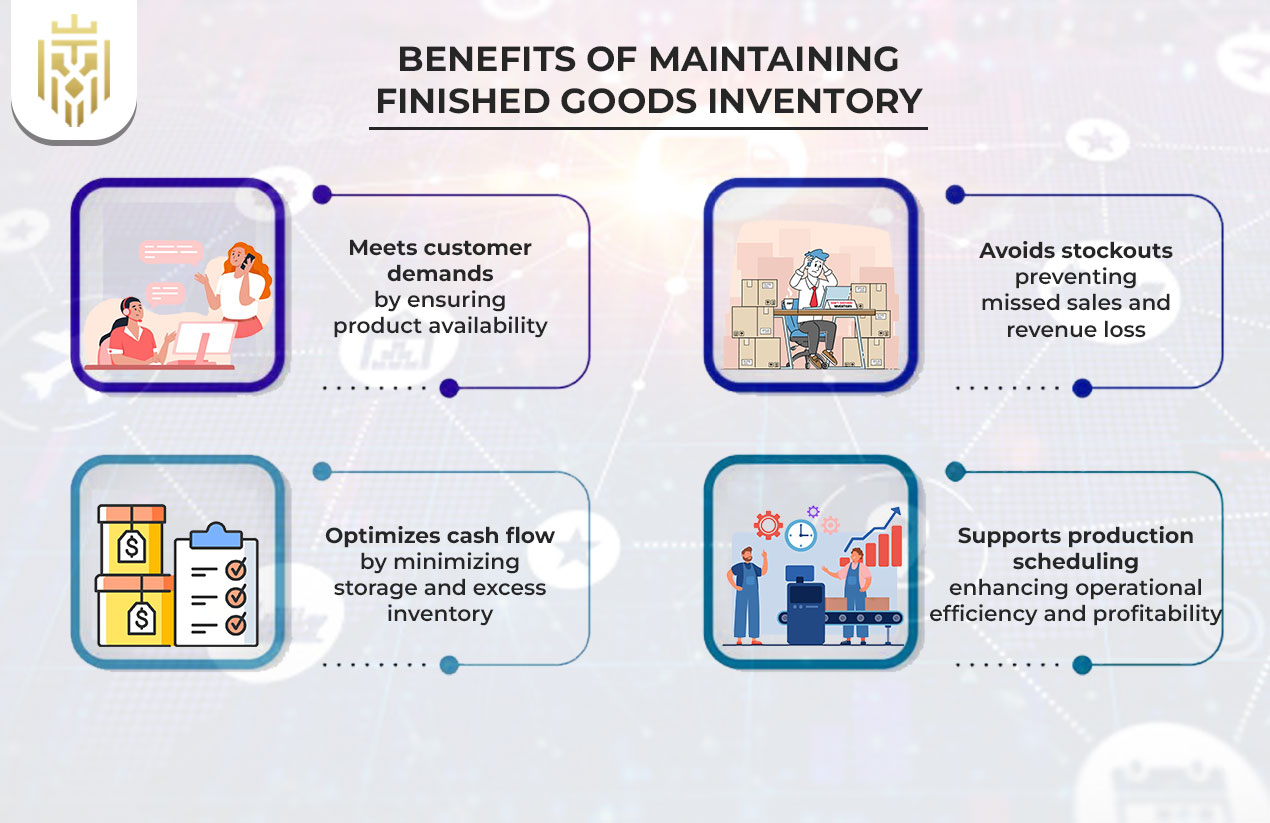
Effectively managing finished goods inventory allows businesses to meet customer demands, avoid costly stockouts, and optimize cash flow by reducing unnecessary storage costs. For example, valley health systems might keep essential medical supplies as finished goods to ensure quick delivery and avoid shortages. Additionally, maintaining proper finished goods inventory supports production scheduling and economies of scale through bulk purchasing, ensuring profitability.
Improved Cash Flow
By keeping good finished goods, the liquidity is improved as the sales turn into revenue faster. Knowledge of what is finished goods inventory enables corporations to determine the value of stock and prevent overproduction. Good inventory management helps in maintaining a consistent cash flow and ensuring that the inventory of goods is at par with customer demand.
Buffer for Demand Fluctuations
Manufactured products are used as a cushioning system in case the market demand changes. Companies can gain an understanding of how to stabilize supply through keeping sufficient inventory. Using a finished goods inventory example highlights how firms absorb shocks during unpredictable markets and meet product requirements without delaying customer orders.
Optimised Inventory Management
An effective stock system will make sure that there will be no surplus or too little inventory. Formula-based calculations allow companies to know the exact materials they need. By aligning finished goods with goods manufactured, businesses strengthen inventory management, control costs, and reduce waste while still meeting customers’ needs efficiently.
Identify Profitability & Budgeting
Finished goods assist businesses to know how profitable they are by determining how much less production costs and sales revenue there are. Accounting data can be used by managers in development planning as well as future projections. Understanding how do you calculate finished goods inventory allows better planning of expenses and more effective allocation of resources.
Reduces Material Waste
Properly maintaining finished goods reduces unnecessary wastage of raw materials. Organizations that focus on inventory definition ensure production is better controlled, which supports sustainability. This reduces wastage of materials, reduces cost, and improves efficiency of supply chains without failure to satisfy the customer demand appropriately.
Tracks Current Assets
Finished goods represent the current assets of an organization, which is important in financial health. They can be monitored by the companies, for example, in accounting records and balance sheets. Using the inventory definition helps managers evaluate how much stock is ready for sale, improving business transparency and resource planning.
What is the Finish Goods Inventory Formula?
The finished goods inventory formula is Beginning Finished Goods Inventory + Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). Accurate calculation requires data on COGM and COGS, and it provides businesses with a clear view of their available inventory.
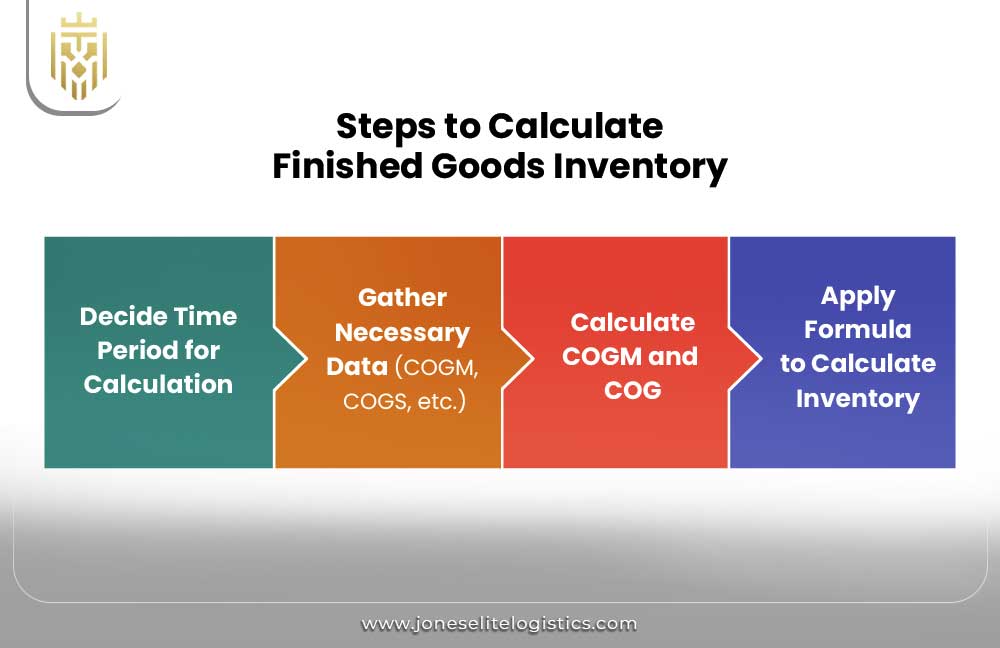
How to Calculate Finished Goods Inventory?
To calculate finished goods inventory, select a consistent time period, then gather COGM and COGS data. Plug these into the formula: Finished Goods Inventory = (COGM – COGS) + Previous Period’s Finished Goods Inventory. Understanding how do you calculate finished goods inventory helps companies, like those in valley health systems, maintain balanced stock levels, supporting efficient operations.
Decide the Time Period:
For accurate calculations, it’s essential to maintain a consistent time period across all inventory formulas. For example, if you’re tracking finished goods inventory for an e-commerce business selling candles with a proper understanding of what is finished goods inventory, decide on a timeframe—like the previous quarter—to assess your inventory levels.
Gather Necessary Data:
To calculate finished goods inventory, you need to gather key data:
-
COGM (Total cost of manufacturing during the period, including raw materials, labor, and overhead).
-
COGS (Calculated as Beginning Inventory + Purchases During Period – Ending Inventory).
In addition, include the time period, inventory records, demand forecasting, and inventory audits to refine your inventory calculations.
Calculate COGM and COGS.:
To calculate COGM, use the formula:
COGM = (Beginning WIP Inventory + Total Manufacturing Cost) – Ending WIP Inventory.
Similarly, calculate COGS using:
COGS = (Beginning Inventory + Purchases During Period) – Ending Inventory. This ensures that the cost of goods produced and sold is properly accounted for.
Calculate finished goods inventory.
Finally, apply the values for COGM, COGS, and the previous period’s finished goods inventory to the formula:
Finished Goods Inventory = (COGM – COGS) + Value of Previous Period’s Finished Goods Inventory.
This final calculation gives you the current finished goods inventory levels.
Steps to Becoming Finished Goods:
Finished goods pass through several stages: from raw materials to work in progress, and finally, to completed products. Managing each stage effectively is critical for efficient production, minimizing waste, and maximizing profitability.

Raw Materials:
Raw materials are essential components that are sourced from natural or synthetic substances. These materials undergo refinement to create products, which are then sold to customers once they reach the finished goods stage.
Work in Progress:
Work in progress refers to items actively being produced, bridging the gap between raw materials and finished goods. Techniques like Lean Production, Quick Response Manufacturing, and Just-in-Time (JIT) are employed to minimize this inventory phase and improve production efficiency.
Finished Goods:
Finished goods are completed items that are ready for sale to customers. Managing this inventory effectively helps businesses generate revenue and profits while minimizing costs associated with holding excess stock through automated inventory management systems.
Best Practices for Finished Goods Inventory
One of the best practices in the handling of finished goods is stability of the systems, including supply chains. Businesses should apply tools like inventory management software, calculate demand accurately, and ensure smooth production cycles. These plans assist in ensuring the goods are in stock and providing sustainable growth in terms of efficiency.

Use Inventory Management Software
Embracing technology makes the processes simplified through the automation of the inventory of goods. Businesses can study the movement of stock and understand improved ways of control. Several organizations like valley health demonstrate how inventory management tools make a difference by helping them improve accuracy, streamline operations, and enhance the decision-making process for overall efficiency.
Optimising Inventory Strategically
Strategic optimization refers to matching completed products with customer requirements without running stocks. Companies study the finished goods inventory examples to identify gaps. This management practice assists in determining the value of goods at the ready to be sold so that there is a balance between supply and demand as well as cost control.
Inventory Audits
Frequent audits will provide proper records of manufactured goods and finished goods. Audit procedures are also cherished by firms with a strict employee verification procedure. Cooperative association practices illustrate the fact that it is important to verify counts and amend discrepancies to avoid losses and enhance improved business planning of inventory.
Automate Ordering Process
Automation is more efficient, as it reduces human error during stock management. Systems inc software helps businesses to make the process of tracking orders and the product flow less complicated. Automated ordering keeps the finished goods stocked, minimizes shortage risks, and ensures that there is a healthy inventory of goods for the customers.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is therefore a process that helps balance the production of finished goods. The businesses are able to use formula models to calculate consumption patterns and stock up. This practice helps rural electric cooperative organizations and others stabilize resources, reduce waste, and maintain smooth operations to meet fluctuating demand efficiently.
Challenges in Handling Finished Goods Inventory
Dealing with finished goods has its challenges, such as expensive cost, obsolescence, and unpredictability of the market. Knowledge in calculating stock needs and what inventory is will assist organizations such as the rural electric providers in addressing inefficiencies. The solutions to these challenges will be long-term sustainability and improved business performance.

Inventory Handling Costs
Storage, transport, and management of the finished goods increase the costs. Goods inventory can be properly tracked to assist businesses in managing their spending. Companies with an established logistics system demonstrate how proper planning can reduce the cost of handling and have products that are available to be delivered.
Demand Variations
Fluctuating demand creates uncertainty in goods manufactured and finished stock. By applying inventory management practices, businesses can learn to handle these cycles effectively. An example of how planning variability is important in industries is background check employment practices, which enable products to be available even when their market patterns are unpredictable.
Obsolescence Risks
Unsold finished goods might not maintain their value. This is usually in the case of old products or trends. Referring a finished goods inventory example, companies can track turnover rates and avoid obsolescence by aligning production with demand and keeping inventory fresh.
FAQs
1. What is the Finished Goods Inventory?
Finished goods inventory refers to fully manufactured products ready for sale to vendors, retailers, or consumers. It is crucial for tracking production, ensuring financial accuracy, and determining product valuation.
2. What is the Importance of Finished Goods Inventory?
Finished goods inventory helps businesses meet customer demand, reduce stockouts, optimize production, lower costs, improve cash flow, determine profitability, and leverage economies of scale through bulk purchasing benefits.
3. How to calculate finished goods inventory?
To calculate finished goods inventory, select a time period, gather data for cost of goods manufactured (COGM) and cost of goods sold (COGS), and apply the finished goods inventory formula.
4. What is the Finished Goods Inventory Formula?
The finished goods inventory formula is:
Finished Goods Inventory = Beginning Finished Goods Inventory + Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). This helps determine the value of goods available for sale.
5. How does finished goods inventory affect a company’s financial statements?
The effects of finished goods inventory on the financial statements of a company are that it will be seen as a current asset, and it will influence the cost of goods sold, profitability, and balance sheet value. It will also show efficiency in the production of the company and efficiency in managing its inventory.