What is Physical Distribution?
Physical distribution is the action of handling the circulation of products starting at the source to the consumption. It involves the warehousing inventory, processing of orders, and management of the inventory and it constitutes an essential component of distribution logistics. This enforces that goods pass smoothly through the supply chain in meeting consumer needs.
Importance of Physical Distribution
Physical distribution has significance in that it influences the customer service, speed and profitability. An effective physical distribution in marketing system leads to reduced cost, improvement in efficiency in distribution logistics, and operations which leads to smooth movement of products through the distribution channels eventually contributing to consumer satisfaction and growth of business.
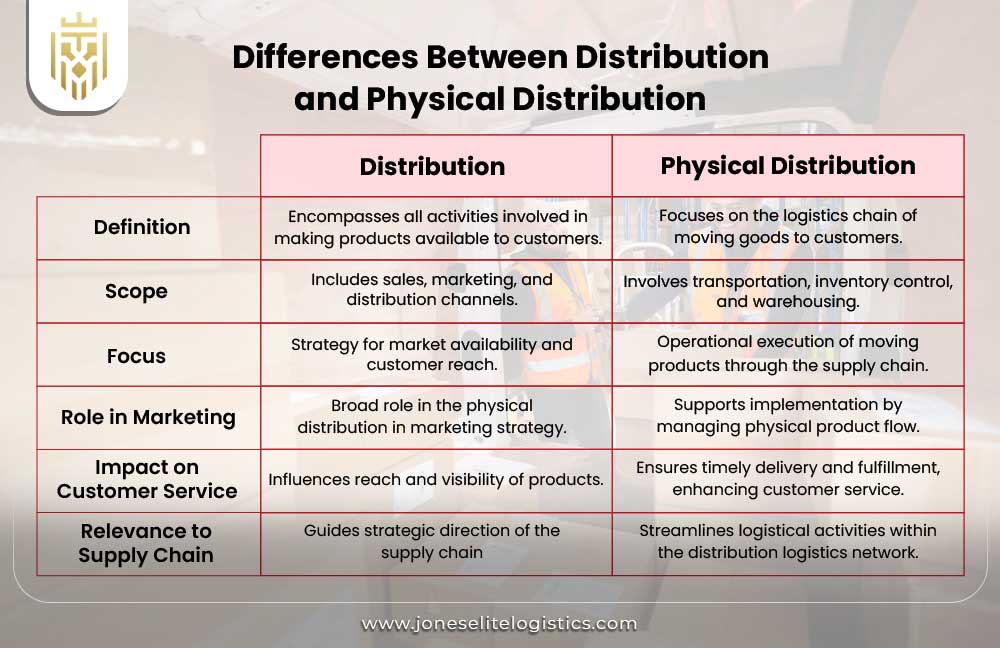
Differences Between Distribution and Physical Distribution
Distribution covers all activities of placing products available, i.e., sales, whereas physical distribution is the chain concerning logistics such as transportation, inventory control, and warehousing. This differentiation is central to the physical distribution in marketing: strategy and implementation, and helps to streamline the supply chain activities and as well as serve the customers with ease.
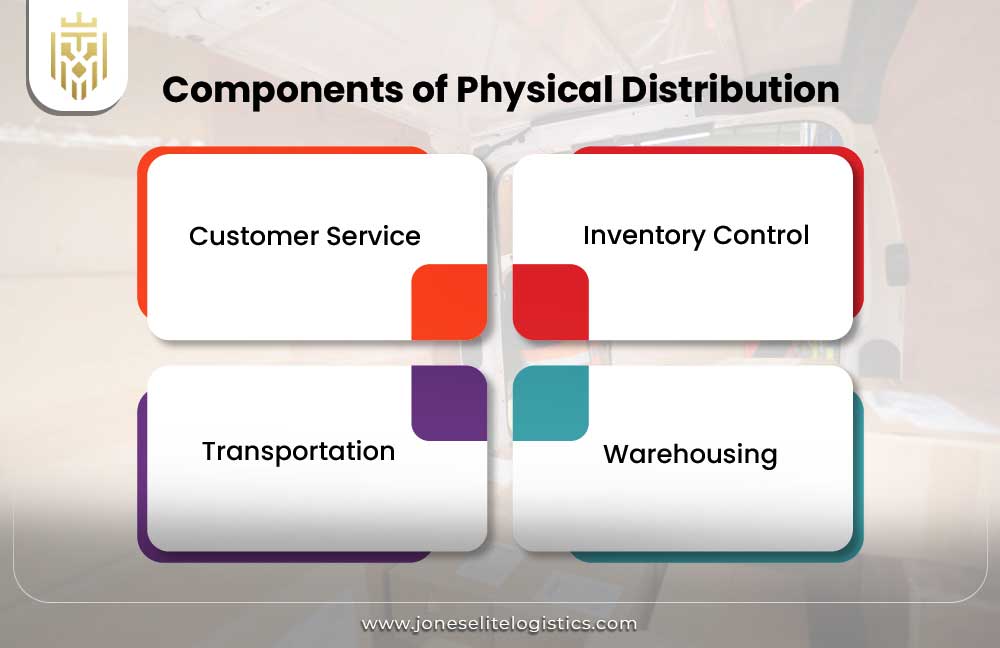
Components of Physical Distribution
The marketing aspects of physical distribution incorporate such vital elements as customer service, inventory, processing, order action, warehousing materials and transportation. All these guarantee smooth movement of products, improvement of logistical activities in distribution systems and also promoting distribution channels of the supply chain.
Customer Service
Customer service plays a key role to achieve delivery standards in physical distribution. It affects every element of physical distribution, making sure that the products are delivered to the customers in time. The presence of high levels of service works to motivate loyalty and customer satisfaction to ensure that distribution logistics are more consumer-driven and responsive at supply chain level.
Inventory Control
Physical distribution makes the right goods available at the right place and inventory control is one of its most important aspects. Appropriate inventory management will reduce costs of holding, eliminate stock-outs, and sustain flow in the distribution logistics, and hence it will enhance a great customer service and increase the overall reliability of the entire supply chain.
Transportation
Transportation is an important component of physical distribution because it takes products through the supply chain. It links factories, warehousing stocks and consumers. The role of logistics in distribution channels is strengthened due to an efficient transportation, which will guarantee reduced costs, faster delivery as well as improved customer service.
Warehousing
Warehousing is an important aspect of any physical distribution as it is a storage and product architect facility. It helps in the processing of orders and gives a chance of improving the inventory control system so that is one of the necessities of physical distribution. High performing warehousing inventory enhances rates of fulfilment and general distribution logistics.
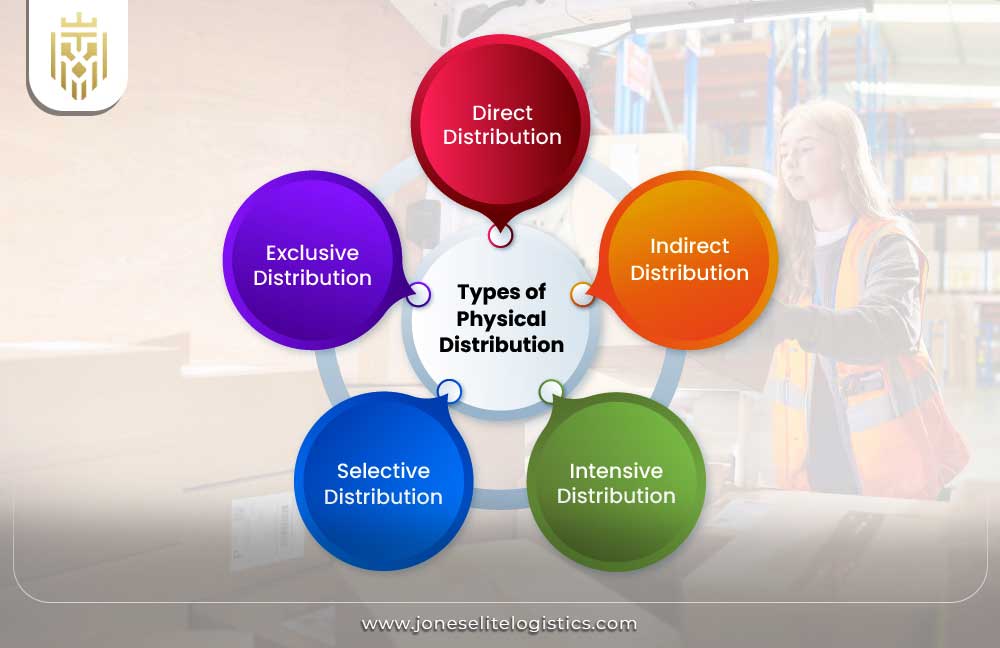
Types of Physical Distribution
Types of physical distribution are direct distribution, indirect distribution, intensive distribution, selective distribution and exclusive distribution. These channels of distribution define the modes of delivering products to consumer based on compromise between customer service requirements, control and market coverage within the chain of supply.
Direct Distribution
Direct distribution denotes the sales of products directly to the consumers, without the third persons being involved, putting the company in the enviable position to control the distribution logistics. Taking control of advertising along physical distribution channels will allow continuity in all distribution lines, but also to hold more responsibility on being accurate in handling inventory volumes and distribution accuracy.
Indirect Distribution
Indirect distribution involves intermediaries to distribute the products to the consumers. The approach relieves the physical distribution pressure on the production house and makes use of institutionalised distribution hubs. It enhances coverage and may undermine customer service control, warehousing stock, and processing orders at the supply chain.
Intensive Distribution
Intensive distribution involves availability of goods through many distribution channels in physical distribution. It makes the product and services easily accessible, particularly with fast-moving consumer goods. This model also demands effective transportation, storage and order handling to run large volumes with high customer service satisfaction.
Selective Distribution
Selective distribution is the strategy by which a firm decides to select particular channels of distribution to retain control of the brand. In this physical distributing model, less partners translate to increased control over the customer service and taking care of the inventory. It is in the middle of universal accessibility and a custom approach to logistics and marketing.
Exclusive Distribution
Exclusive distribution restricts product distribution to a few partners. This physical distribution strategy builds brand reputations and makes the distribution of the product easier. It facilitates luxury customer experience, stricter control over inventory, and warehouse inventory and order processing in the supply chain.
Factors that affect Physical Distribution
The major issues affecting physical distribution are: product durability, product size, warehouse management systems, and transportation. These have impact on the logistics planning, inventory in warehouses and order processing and thus it works out efficiently and leads to improved customer service within the distribution logistics network.
Product Durability
Physical distribution (proofs on how and at what pace) is dependent on the quality of products. Weaker products require more attention when it comes to inventory and speedier transportation. Durable goods also ease the distribution logistics since they are easier to move up the supply chain and are relatively cheaper with the available methods of distributing them.
Warehouse Management Systems
Warehouse Management Systems also enhance physical distribution through better inventory control, order processing and accuracy of operations. These systems limit mistakes and improve customer service, establishing a high-tech core in logistics in distribution in the modern world and promotes the smooth movement throughout the chain of supply.
Product Size
The size of a product has a lot of influence on the physical distribution in transport, storage and packaging. Bigger products are more costly to stock and manage in warehouses and smaller products might require special handling. Proper planning contributes to even distribution of cost in the distribution logistics and maximisation of overall customer services.
Transportation
The factors that affect transportation efficiency in physical distribution are cost, safety, speed and infrastructure. Effective strategic planning makes the process of movement through the channels of distribution timely, enhances customer service, as well as advanced inventory management. It is an important connection in ensuring there is movement in the supply chain.
Advantages Of Physical Distribution
An efficient physical distribution leads to a better management of the inventory, a higher customer satisfaction, a decrease in the inventory holding cost and general cost. Such advantages enhance the effectiveness of the supply chain, makes orders easier to process and make its distribution logistics tighter to serve better and make more money.

Enhanced Inventory Management
The existence of strong physical distribution systems facilitates better inventory management, cutting down costs and designing the inventory levels. It keeps the supplies where they are required improving customer service and logistics chain efficiency, especially in streamlining warehousing inventory and distribution order processing activities.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Efficient physical distribution will result in quicker delivery and orders and proper customer service. Happy customers will most likely be repeat customers to increase overall success. Loyalty is achieved through effective management of the distribution channels and inventory which in turn assists the competitiveness of supply chain.
Reduced Inventory Holding Costs
The cost of holding inventories will be minimised through effective delivery of goods. Intelligent inventory reduces storage, insurance and obsolescence costs. The advantage of this lean method to businesses is that it reduces the stocks in any said warehousing operation, increases cash flow, and that better flow in the distribution logistic network.
Faster Market Responsiveness
The faster market demand and orders of customers are met through a properly implemented physical distribution system. The effective management of the distribution process, inventory tracking, ordering operations helps business to change rapidly, lower lead time and enhance customer service throughout the supply chain.
FAQs
1) What is Physical Distribution?
Physical distribution is the action of handling the circulation of products starting at the source to the consumption. It involves the warehousing inventory, processing of orders, and management of the inventory and it constitutes an essential component of distribution logistics.
2) What are the components of physical distribution?
The marketing aspects of physical distribution incorporate such components as customer service, inventory, processing, warehousing materials, and transportation.
3) What are the factors of physical distribution?
The major issues affecting physical distribution are: product durability, product size, warehouse management systems, and transportation.
4) What are the types of Physical Distribution?
Types of physical distribution are direct distribution, indirect distribution, intensive distribution, selective distribution and exclusive distribution.