What Is Cargo Theft?
Cargo theft involves acts of criminality where goods or merchandise are taken from under transit, at storage points, or through some means of fraud. Theft compromises logistics operations worldwide by targeting trucks, containers, rail shipments, or any system supporting logistics electronically. In India and other fast-growing markets, e-commerce growth and high-speed intercity distribution have turned cargo theft into an even more serious supply-chain risk. Preventing cargo theft entails proactive strategies, with several layers of physical security and digital surveillance to protect the high-value freight on its journey.
What happens when there is a cargo theft?
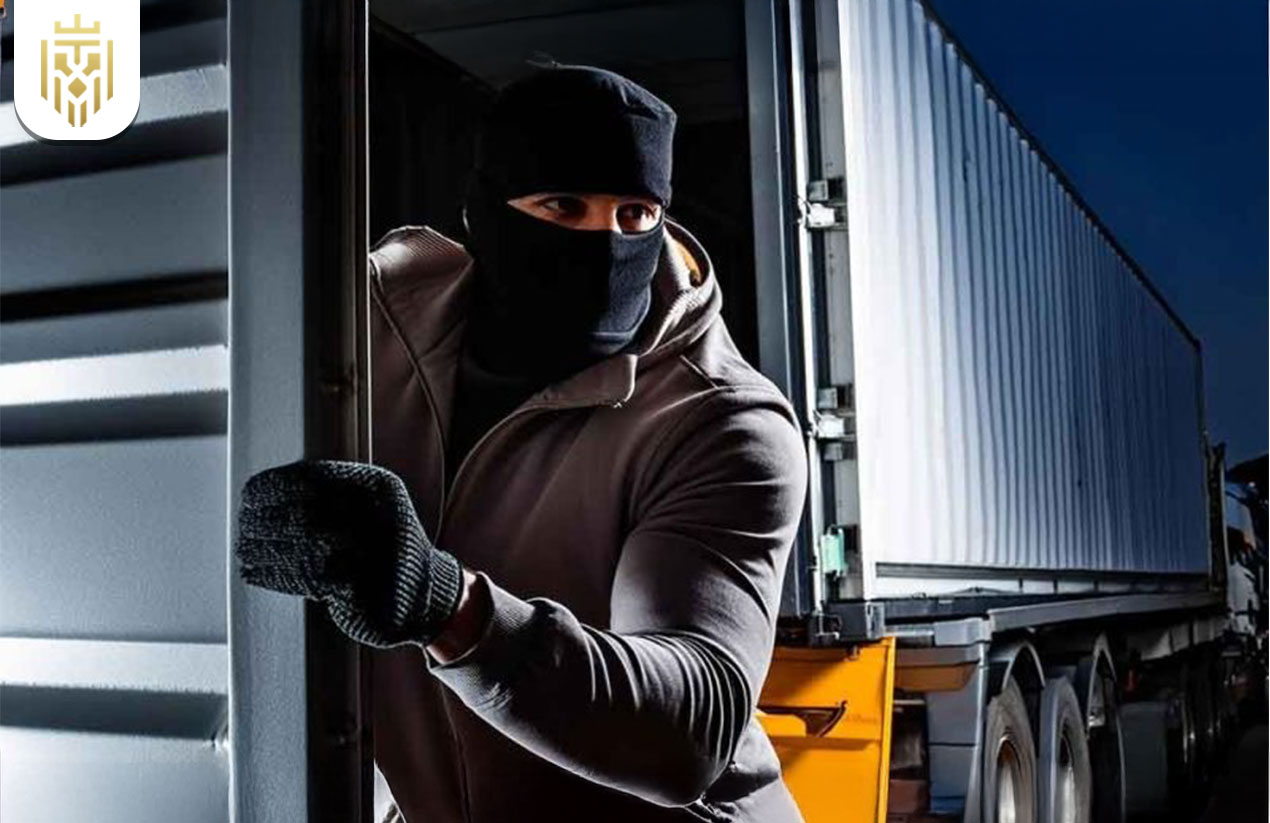

When theft occurs, the consequences go far beyond missing goods—it causes ripples across operations, finances, and trust.
Causes massive financial loss
Cargo theft usually alludes to product loss and cost of reclamation, which in turn puts pressure on margins and insurance premiums. An isolated incident might produce damages amounting to lakhs or even crores in the case of extremely high-value goods.
Disrupts supply chain operations
Unexpected theft delays deliveries, affects inventory levels, and halts production lines, leading to inefficiencies and customer displeasure in time-sensitive industries.
Damages brand reputation
An expectation of customers is the fulfilment of orders and reliability. In cases when a cargo theft causes orders to be delayed or not delivered at all, it kills the last ounce of trust and possibly business relationships.
Poses safety and insurance risks.
Sometimes, cargo theft brings along violence and internal fraud, raising employee safety concerns and complex insurance claims for the companies. It increases exposure to legal and compliance issues, especially cross-border shipments.
Key Documents at Risk During Cargo Theft
Cargo theft isn’t always just about the products. Important documentation is also targeted, which can further complicate operations and claims.
Bill of Lading
It is a bill of ownership and receipt of goods improperly taken because it might have been used to claim ownership fraudulently.
Delivery receipts
These serve as confirmation of good delivery. Absence or forgery of such receipts could result in confusion or cases of false claims.
Shipment tracking records
Departure data is useful for thieves who intend to reroute or intercept cargo. Dispersing such information greatly reduces the chance of recovery.
Cargo insurance papers
Without the insurance documentation, claims might be delayed or denied, exposing the business.
Packing lists
These provide detailed records of what was shipped. Any interference with these lists may affect customs clearance and inventory reconciliation.
Export/import declarations
Taken declarations can cause compliance issues and create additional scrutiny from customs, especially in an international shipment.
Common Methods of Cargo Theft

Thieves use both physical and digital strategies to intercept cargo. Understanding these methods helps businesses identify weak points in their logistics chain. Smaller items are discreetly removed while goods are being loaded, unloaded, or during short halts.
Hijacking and truck theft
With the use of guns, the gangs may forcibly seize trucks in transit along deserted routes or during the hours of night halts.
Fictitious pickups
Dishonest carriers, pretending to be legitimate, pick up shipments with fake IDs or documents and disappear before the perpetrators can be detected.
Warehouse break-ins
Poorly secured warehouses make easy targets, especially if access points and surveillance systems are not managed well.
Cyber breaches targeting logistics data
Hackers may infiltrate shipment data and manipulate delivery information to have the cargo diverted or intercept it.
Insider threats
When employees or contractors leak information or aid in the theft, internal security measures become essential.
Pilferage during transit or loading
Smaller items are discreetly removed while goods are being loaded, unloaded, or during short halts.
Smart Prevention Measures
A proactive approach, combined with reliable partnerships and smart technology, can drastically lower cargo theft risks.
Conduct route risk assessments
When considered unarguably, shipping lanes should be assessed for risk levels, especially those in supposedly high-theft zones. Depending on the risk levels, other routes may be chosen, whenever practicable, so that alternative or safer routes can be utilised.
Vet all third-party logistics providers
Ensure that all transporters, drivers, and warehouses adhere to security standards and are contractually bound to maintain such procedures.
Secure facilities and parking locations
Select only stops with guard services and CCTV monitoring for rest breaks or overnight halting. Avoid those without control.
Use GPS and geofencing technologies
Real-time tracking allows for live location visibility, and geofencing can trigger alerts when vehicles deviate from assigned routes.
Seal containers and monitor for tampering
Use a tamper-proof seal and check for any sign of unauthorised access during the shipment.
Train drivers and staff on security protocols
Train logistics operators on fraud, their responses in emergencies, and how to report suspicious activity.
Best Practices to Mitigate Cargo Theft

Strong planning and disciplined operations help create a secure logistics network that keeps theft at bay.
Schedule deliveries in daylight hours
Most thieves operate at night, taking advantage of poor visibility. Scheduling deliveries in the daytime enhances security and mitigates risk.
Avoid predictable routes and routines.
Organised crews may easily be targeted if the shipping times, drivers, or routes remain constant for even a short duration.
Split high-value shipments
Divide precious cargo into smaller lots to eliminate the possibility of losing everything in a single transit incident.
Work closely with law enforcement.
Work out a network of contacts with the local police and customs authorities, particularly when shipments travel high-risk or different routes.
Implement strict access control and surveillance
Limit access to only authorised personnel and keep a digital record of personnel entering and exiting.
Invest in tamper-evident packaging
Seal packages in a manner that, should they be illegally accessed, such breaches are entirely obvious, and corrections can be made immediately.
Role of Insurance & Legal Support
Strong legal and financial backing ensures business continuity even when theft occurs despite preventive steps.
Financial recovery from losses
Cargo insurance makes it possible to recover part or all of the loss while lessening the financial burden of theft incidents.
Claims processing and documentation
Promptly reporting well-documented reports helps speed up the insurance claims settlement process.
Legal liability coverage
Good insurance also protects the business from the legal consequences of non-delivery or breach of contract.
Support for cross-border theft cases
The legal fraternity, along with the insurance side, helps in dealing with the international incumbencies concerning cases involving customs or jurisdictional challenges.
Emerging Tech Against Cargo Theft
Technology continually innovates with cargo protection in transit, from tracking to alerting.
Real-time GPS tracking and alert systems
Tracks the shipment along the route and immediately alerts the concerned authorities of any deviation in the route or suspicious stops.
RFID-based seal tracking
Uses RFID to keep track of seal breakage and tampering during transit.
AI-based route optimisation
AI uses historical data and predicts adjusted routes that are safer and more efficient, placing them at lesser risk.
Blockchain for tamper-proof documentation
It creates immutable digital records and mutes all possibilities to forge or alter details of shipments.
Telematics and remote shutdown systems
These systems afford advanced remote truck shutdown in case of unauthorised access or hijacking.
FAQs
1. What are the most common types of cargo theft?
Truck hijacking, fictitious pickups, insider theft, and break-ins into warehouses are the most common modes of operation by cargo thieves.
2. How can companies prevent fictitious pickups?
Check credentials of transporters, use a digital proof-of-pickup system, and create safe channel communications.
3. What role does technology play in preventing cargo theft?
Technology allows real-time monitoring, route alerts, and tamper detection and has increased security capabilities by tracking systems, AI, and encryption.
4. Is cargo theft covered by standard insurance policies?
Most insurance plans cover cargo theft cases, but for their valid application, terms and conditions must be carefully read and complied with.
5. How should a business respond after a cargo theft incident?
Immediately report to the police and insurance company, adequately document the incident, inform stakeholders, and adjust security plans to prevent recurrence.
6. What is cargo theft?
Cargo theft is the unlawful stealing of goods occurring during transport or storage, often in the form of physical theft, fraud, or cyber manipulation.