What is Freight Bill?
A freight bill is a crucial financial document used in the logistics industry to specify charges and transaction information in shipping and service terms between shippers and carriers. In contrast to a bill of lading, it emphasises the invoicing factors, which make the freight billing process as precise as possible and transparent in tracking all the cargo flows.
Elements in a Freight Bill
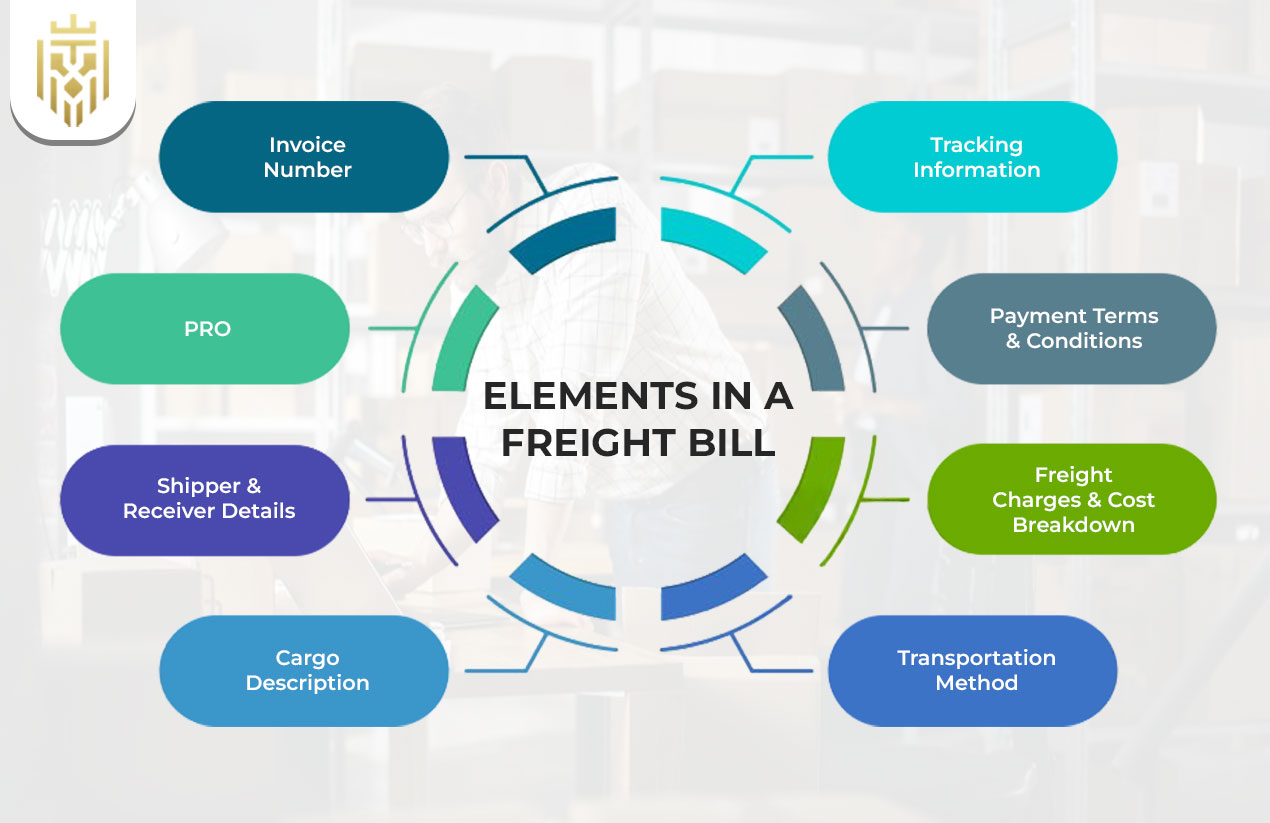
The freight bill format contains important information, such as invoice numbers, information of the shipper and receiver, a description of the cargo, charges and details of the service levels. All these factors guarantee cost-effective and timely delivery, appropriate validation, and adherence to shipping terms and conditions in organised carrier services environments.
Invoice Number
The logistics invoice has an invoice number which can easily be identified and referred to. It connects payment and shipping transaction information and records and avoids duplication. This aspect makes the freight billing process accurate and promotes freight broker activities and audit compliance throughout the movement of the cargo.
PRO
The PRO number relates shipments to the bill of lading number and makes it easier to identify shipments in tracking and carrier services. This minimises mistakes during the freight billing process by authenticating cargo information, enhancing efficiency, and providing better payment and compliance oversight of multiple cargoes.
Shipper & Receiver Details
The pickup and delivery address is important in a freight bill format. Such information reduces delays, ensures safe, timely delivery, and assists in adhering to shipping terms and conditions to avoid conflicts, mistakes, and misunderstandings during the logistics process by both shippers and carriers.
Cargo Description
The cargo description contains information about the product, such as weight, size and contents. It helps in the identification of itemised cost breakdown, facilitates the adherence to special shipping services and improves the accuracy in the freight billing process to avoid delays in the shipping cycle.
Transportation Method
The chosen transportation mode—air, road, sea, or rail—affects freight bill format entries. It also has an implication on the itemised cost breakdown structures, delivery schedules, and service-level details that help clarify stakeholders about their responsibilities and aid efficiency in the overall operations of the carrier services within networks.
Freight Charges & Cost Breakdown
A detailed itemised cost breakdown in the freight billing process highlights transportation, fuel surcharges, and handling charges. This is to provide clarity in shipping transactions, to enhance accountability, and to ensure that costs are correctly matched to the payment terms to reduce conflicts between shippers, carriers, and freight intermediaries.
Payment Terms & Conditions
The terms of payment specified in the freight bill provide schedules, methods and penalties. Combined with shipping terms and conditions, they provide financial transparency, facilitate payments and build trust among carrier services, shippers and freight intermediaries through the establishment of organised rules addressing financial compliance.
Tracking Information
Shipment status updates are linked to the tracking information that correlates to the PRO or bill of lading number. It offers real-time service-level information, verifies secure and punctual shipment, and provides visibility, enhancing partnership within the shipper-carrier-broker nexus of the freight-billing procedure.
Importance of Freight Bill in Logistics
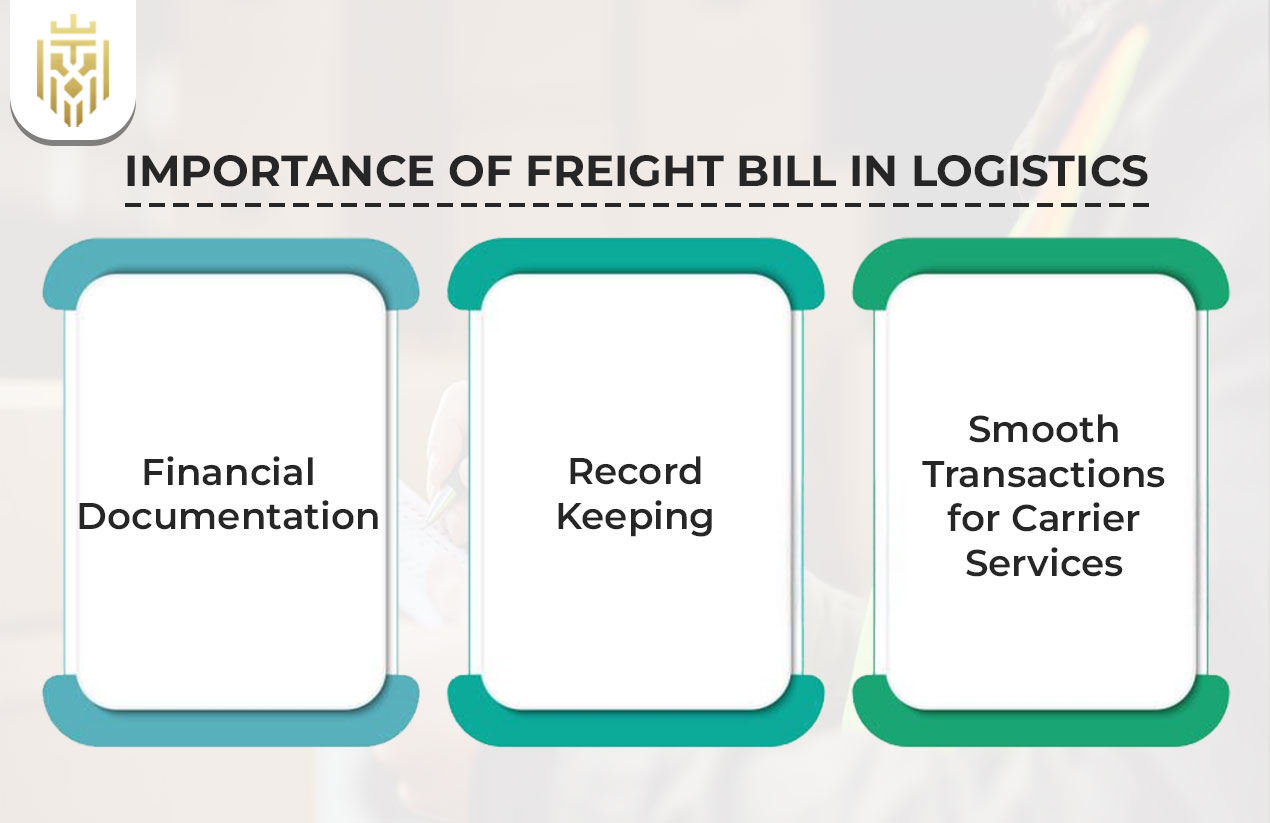
A freight bill is an inevitable element in logistics that records the details of transactions during shipping, attests to the terms and conditions of shipping and promotes specialised shipping services. It provides greater visibility, proper costing, and serves as a formal financial document in logistics that promotes compliance, audit, and efficient cash flows.
Financial Documentation
As a logistics financial document, the freight bill ensures that all the transactions are properly captured, including charges, payment terms and transaction details in shipping. This framework aids in audits and contributes to the accountability of the business and its appropriate management practices to ensure long-term financial welfare.
Record Keeping
Freight bill format record keeping provides visibility of previous shipments, pickup and delivery addresses and charges. These archived records facilitate compliance, ease reconciliations, and assist companies in analysing carrier services to facilitate informed decision-making and minimise future billing errors.
Smooth Transactions for Carrier Services
Effective billing creates efficient settlements of carrier services. A properly designed freight billing system brings about transparency, minimises conflicts and helps in safe and timely shipment. Through the harmonisation of shipping terms and conditions, shippers and carriers build trust and simplify the long-term operating relationship.
How does Freight Bill differ from Bill if Lading?
A freight bill and bill of lading number are not similar terms that are used interchangeably. Although a bill of lading is a legal shipping agreement, the freight bill is a shipping invoice that is only concerned with charges, payment terms, and financial validation.
Bill of Lading
The bill of lading is a legal document in the logistics industry, which includes information about a pickup and delivery address, cargo description, and liability terms. It approves shipment and confirms receipt but does not include the itemised cost breakdown or settlement-specific details as does the freight bill.
Freight Bill
The freight bill format places emphasis on invoicing and transactional information in shipping and records service-level information and payment terms. Contrary to the bill of lading number, it is not a contract unless it is a financial document used in logistics to settle bills.
Common Challenges in Freight Billing
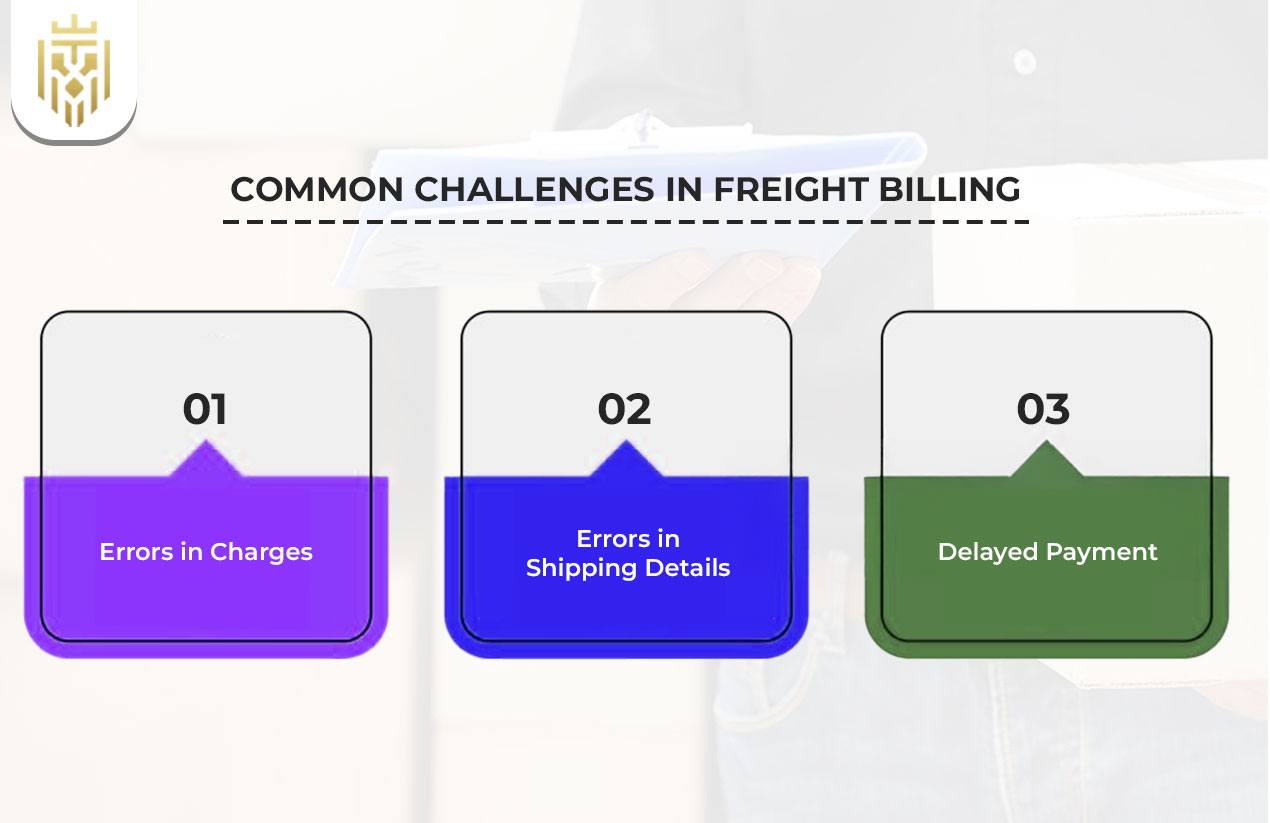
Some problems with the freight billing process may include wrong detail of transactions in shipping, mismatch in bill of lading number, and settlement delay. Any error in the format of the freight bill enhances arguments, which make shippers, carriers, and freight brokers pay more and experience inefficiencies.
Errors in Charges
Mistakes in an itemised cost breakdown lead to disputes. Manual errors in the freight bill are in most cases the cause of inaccurate billing. This introduces issues with payment conditions, lengthening of timeframes and affecting the trust between shippers, carriers and logistics intermediaries.
Errors in Shipping Details
The misstatement of the freight billing may occur due to the incorrect pickup and delivery address or description of the cargo. Such mistakes cause a mismatch between shipping terms and conditions, unsafe and untimely delivery and add complexity during reconciliation with the bill of lading number in a logistics operation.
Delayed Payment
Billing is usually done manually, which slows down the payment terms, causing disagreements. Errors are added by missing transaction information in shipping or misaligned service-level information. Digital automation will address these problems, including accelerated settlements, enhanced carrier services, and enhanced visibility on both shipper and intermediary sides.
Best Practices for Freight Bill Management
The freight billing process should be managed effectively with the help of digital solutions, audits, and compliance with shipping terms and conditions. An efficient freight bill format not only ensures accuracy but also enhances compliance and ensures safe and on-time delivery for both the carriers and specialised shippers.
Digital Freight Billing & Automation
Automation minimises human error, accelerates the freight billing process, and enhances accuracy on transaction details in shipping. Digitising the bill of lading number with digital systems provides visibility, removes duplication of work and allows specialised shipping services to streamline financial operations efficiently.
Regular Audits
Audit procedures ensure the verification of freight bill format information such as itemised cost breakdown and service level information. Frequent checks enhance accuracy, minimise fraudulent payments, and enhance financial document reliability in logistics, which ensures adherence to carrier services standards and long-term financial responsibility.
Align With Shipping Terms & Conditions
Compliance with shipping terms and conditions would make the freight bill reflect the terms and conditions of payment and transaction in shipping. The benefits of this practice are enhanced trust, compliance, and safe and timely delivery, as it helps to reduce the number of disputes among shippers, carriers, and freight intermediaries.
FAQs
1. What is a freight bill and why is it necessary?
A freight bill is a logistics document that describes the charges, cargo, and the terms of payment to ensure transparency, compliance, and seamless payments between freight shippers, freight carriers, and freight brokers.
2. How does freight bill processing improve logistics efficiency?
An effective freight billing process reduces errors, ensures transactions are properly defined in shipping, provides accurate itemised cost breakdowns, and facilitates quicker payments, which leads to improved visibility, safe and on-time delivery, and enhanced trust in logistics operations.
3. What’s the difference between a freight invoice and a freight bill?
A freight bill is a logistics invoice and lists charges and details of service levels, whereas the bill of lading is a legal document in logistics that defines shipment contracts, responsibilities, and liability.
4. What specifications are included in a freight bill?
A freight bill form has invoice numbers, pick-up address, delivery address, description of the cargo, bill of lading number, detailed cost breakdown, terms and conditions of shipping, description of level of service and clear stipulated payment terms.