Various Stages of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is the cornerstone of the successful functioning of a business. It consists of a series of interlinked processes that guarantee the smooth transition of goods and services from the producer to the end user. Every stage is very important in helping to keep the entire supply chain running smoothly and the quality high while all customers are satisfied.
The supply chain is more than just a product movement; it is a complex system of coordination, strategy, and technology that connects the suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, and customers. It is essential for businesses to see the whole picture of supply chain management, as it allows them to develop a more robust and responsive network that facilitates both the growth and stability of the company.
Planning in Supply Chain
Supply chain management has planning as its first and most important stage. It encompasses devising techniques to balance supply with demand, optimise resources, and keep operations consistent. Planning allows organisations to cut down on waste, correct their forecasts’ accuracy, and attune their production goals with the market trends.
Key Aspects of Planning
Good planning is to a large extent based on forecasting, inventory control, and resource utilisation also for the purpose of customer satisfaction. These are the major five elements in a supply chain that is proactive and well structured.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting makes it possible to estimate future customer demands based on past purchases and market trends. It is only by having accurate forecasts that companies will be able to timely prepare production schedules and also manage their stock inventory in a way that ensures quick response to market changes without risking overstocking or under-stocking.
Inventory Control
Inventory control makes sure that the right products are there when they are needed without tying up funds in excess stock. The process involves checking stock on hand, creating reorder points for each item, and using advanced tracking systems to avoid shortages or surpluses. A strong inventory system helps to improve cash flow and operational flexibility.
Resource Allocation
Resource allocation means that the entire supply chain is getting the most out of labour, materials, and equipment. By having the right up and down movements of resources, letting companies choose which ones to do first and which ones to do later, they can effectively erase things that would slow the process down and thereby reduce the overall costs. The result is the same in both cases, though, i.e., productivity and quality of service are improved.
Process Optimisation
Process optimisation focuses on improving every stage of the supply chain through technology, automation, and performance tracking. Continuous assessment of workflow efficiency helps reduce delays, minimise waste, and strengthen coordination between departments.
Importance of Supply Chain Planning
The framework of supply chain planning ensures the smooth operations and stability of the company in the long run. It sets a common target for all the departments, starting from purchase to delivery. Poor planning can lead to even slight inefficiencies turning into large disruptions, which will negatively affect both cost and customer trust.
Sourcing in Supply Chain
Sourcing is the part of the process where companies determine what suppliers to work with and acquire the necessary materials for their production. This in turn decides the quality, price, and dependability of the whole supply chain. Well-thought-out sourcing methods lead to better and stronger organisations that are able to stay in the race of global markets.
Key Elements
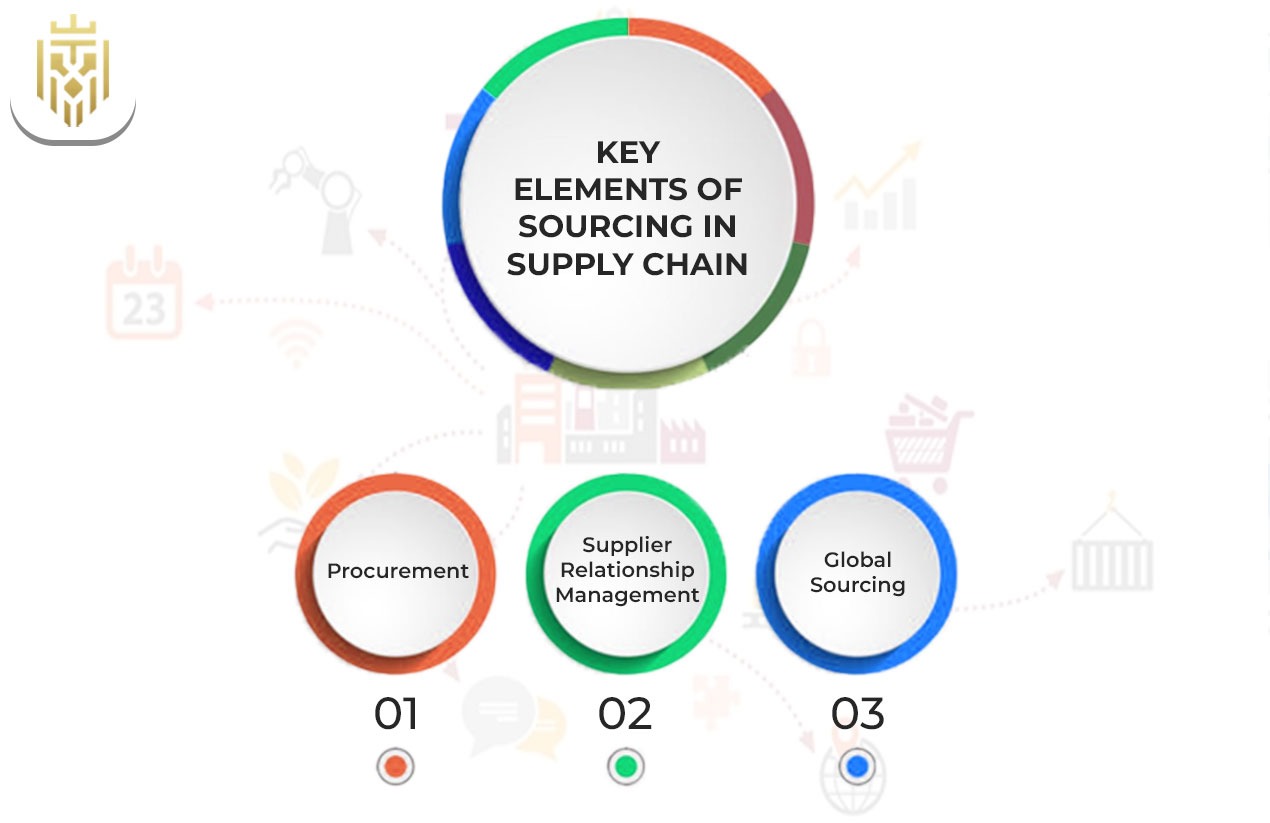
The process of sourcing that ends with saving a lot of money taken up by suppliers consists of supplier identification, negotiation and industry co-operation. On this, continuous monitoring from the side of the company also plays its part in getting price reduction and quality enhancement.
Procurement
‘Procurement’ is a term which refers to the purchase of raw materials, components and services. Supplier evaluation, contract-setting, and material-checking of the production requirement are the main steps here. A transparent and ethical procurement process goes a long way in supporting both cost control and sustainability.
Supplier Relationship Management
Good connections with suppliers guarantee equal quality and deliveries on time. Supplier relationship management fosters co-operation, trust, and open communication, thus resulting in enhanced performance and lowered chances of disruption.
Global Sourcing
Global sourcing is a process that opens a company’s curtain to the international markets, thereby allowing it access to not just the best materials but also the most competitive prices and specialised expertise. This, however, is not without its risks in the form of geopolitical, logistical and regulatory challenges. Effective global sourcing helps a company to become more agile when it comes to responding to global challenges.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the supply chain’s operational core where the transformation of raw materials into finished products takes place. This phase sets the standards for product quality, cost structure and production rate. A manufacturing process that is effective and efficient enables the firm to supply its customers promptly without sacrificing quality.
Key Elements
Manufacturing’s key elements are planning, process optimisation, quality checks, and cost control, which are structured and coordinated. All these elements work together to ensure the production system is efficient and profitable.
Production Planning
Production planning is the practice of matching manufacturing output to demand as forecasted. This means that the production run must be scheduled, capacity must be managed and suppliers must be coordinated. A good plan guarantees that resources are used in the best way possible, which leads to less idle time and waste.
Improving Efficiency
Technology, automation, and lean management principles are the main sources of efficiency in manufacturing. Continuous improvement projects, along with training of the workforce, lead to higher production and product uniformity, which in turn lowers errors and downtime.
Quality Control
Quality control is a process that protects product quality through testing, inspection, and compliance monitoring. The practice of exercising strict quality control creates consumer loyalty, lowers returns, and assures customer satisfaction.
Cost Management
Cost management that is effective helps to keep production financially viable. By operating at lower costs, companies can still deliver quality and efficiency by reducing waste, improving equipment utilisation, and streamlining processes.
Delivery Process
The delivery process is the movement of finished products from production to the customer. It is an important step that decides if a company can keep its promise to the customers in time. A well-coordinated delivery process can make service assurance stronger and brand reputation better.
Key Aspects of Delivery
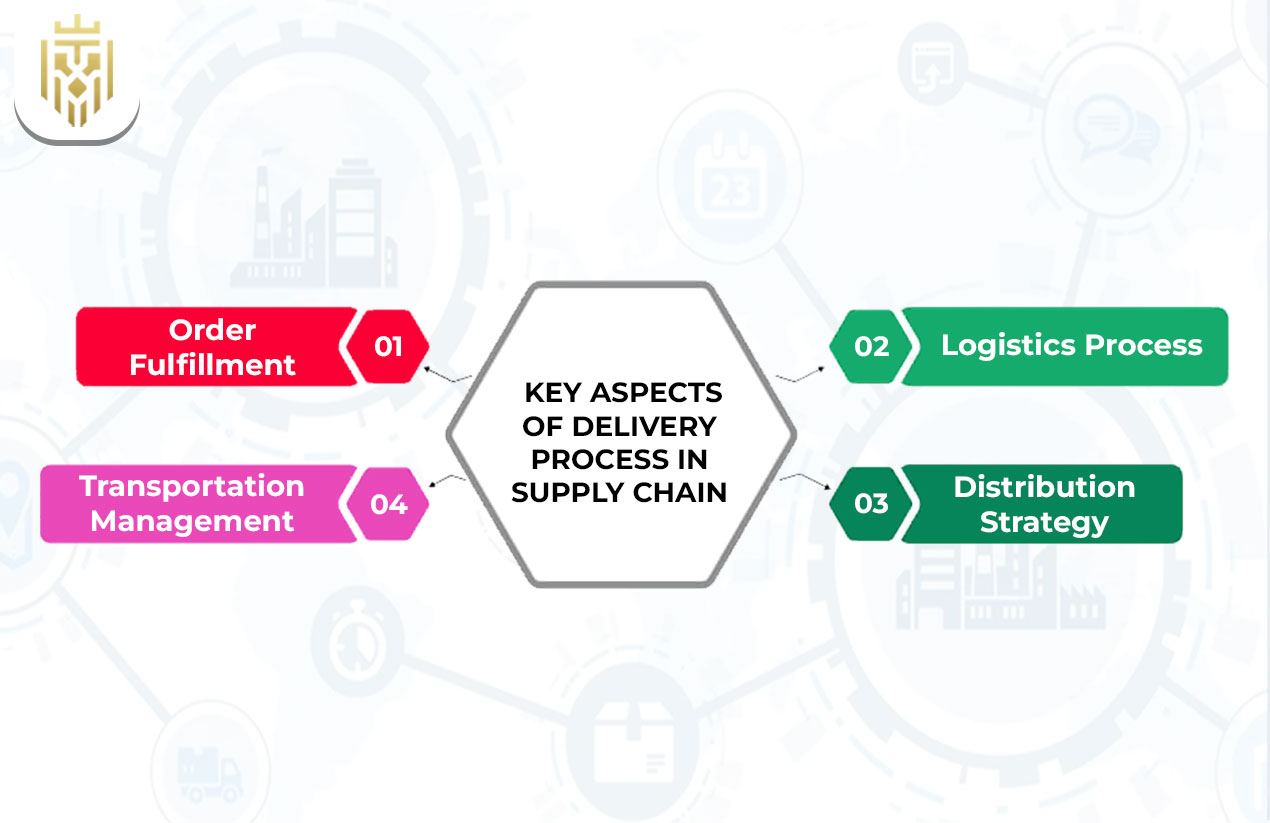
Delivery consists of order fulfilment, logistics collaboration, distribution planning, and management of transport. Each part is very important in making sure the goods get to the customers quickly and in perfect condition.
Order Fulfilment
Order fulfilment is made up of processing, picking, packaging, and shipping the products correctly and quickly. Good systems reduce mistakes and deliver on time, which in turn influences customer happiness and their willingness to return.
Logistics Process
The logistics process is responsible for the whole movement and keeping of goods from warehouses to customers. It makes use of technology, route mapping, and trustworthy carriers to make sure the deliveries happen on time and are economically efficient. Smooth operations in logistics shorten the time goods are in transit and increase the company’s visibility in the network.
Distribution Strategy
The distribution strategy decides the channels of how products go to different markets and customer groups. It can be direct delivery, or through distributors or even third-party logistics, but the chosen method has to consider speed, cost, and service quality in order to be competitive.
Transportation Management
Transportation management arranges for goods to be transported in an effective manner while keeping up with the costs and reducing the impact on the environment. It is possible for businesses to deliver their products faster and in a more sustainable way by choosing the best routes, reliable carriers, and appropriate modes of transport.
Returns Management
Returns management is also referred to as reverse logistics, which involves the journey of returning products from the customer to the company. It mainly comprises of recovery, recycling, and customer service. When returns are managed correctly, businesses can get back their value, retain the customers, and have less waste.
Key Components of Returns Management
A solid return management system guarantees that the processes of handling damage, defective and needless items are very smooth. Moreover, it helps companies keep their operations open, control their expenses and give customers even more confidence in the company by providing efficient after-sales service.
Return Policy Management
A return policy that is both clear and fair creates customers’ trust and makes the return process less complicated. It specifies the criteria for eligibility, the period of time for returns, and the refund procedures, thereby making it certain that both parties know their roles and duties.
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics refers to the transfer of goods from the consumer back to the producer or supplier. It also includes the diagnosing, mending, repacking, or recycling of the returned items. Integrating an effective reverse logistics system into your operations not only benefits the environment but also allows you to recover your costs.
Customer Support
Customer support is one of the most important factors that facilitate the smooth management of returns. When customers receive prompt and friendly service, businesses not only get the chance to change a potentially negative situation into a positive one but also to strengthen the customer bonds and keep them.
Importance of all the Stages of Management

Each stage of supply chain management is interconnected and equally essential for operational success. Together, they ensure efficiency, consistency, and resilience, helping businesses remain competitive in fast-changing markets.
Reduced operational costs
The companies while optimising every stage − from planning to returns − can spot the inefficiencies, waste the least, and manage their expenses. To direct profit margin improvement are the savings.
Increased resilience against disruptions
A well-organised supply chain puts the whole business in a position that they can cover all types of disruptions like scarcity of supplies, delay in transport, or change in markets. This very resilience secures continuity and the accompanying long-term sustainability of the business.
Stronger supplier and customer relationships
The allied trust and transparency are the results of the effective collaboration across all the stages. Consequently, the cooperation with suppliers and customers is an already existing reliable, and responsive network.
Higher customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is bound to rise if products are timely delivered, the quality is preserved, and returns are handled proficiently. Moreover, a well-managed supply chain secures customer loyalty and generates more sales.
FAQs
1. Why is inventory control critical in supply chain planning?
Inventory control prevents the company from having too much or too little stock, which in turn enables a smooth running of operations and an even flow of cash. It allows the power of demand to be harnessed while keeping waste and storage costs low.
2. How do global sourcing strategies affect supply chain resilience?
Global sourcing is a strong factor in the resilience of the supply chain since it not only increases the number of suppliers but also provides better-quality resources. It is, however, necessary to have risk management strategies that will be able to deal with the logistical and geopolitical challenges in a smooth and effective manner.
3. What role does sustainability play in supply chain management?
Sustainability is the main factor that guarantees the responsible operation of supply chains—by means of waste reduction, resource conservation, and ethical sourcing practices. It not only brings about an improved brand image but also results in the company’s operations being in conformity with the long-term environmental objectives.
4. How does reverse logistics create business value?
Reverse logistics enables companies to be reimbursed through its various methods such as repairing, refurbishing, and recycling. It also has the extra benefits of waste lowering, customer trust boosting, and environmental initiatives supporting, thereby contributing to the overall business value increase.









