Understanding Offshoring
Offshoring is where business activities, including manufacturing or services, are transferred to other countries to gain access to cost reduction and competitive labour forces. It is significant in the contemporary global supply strategies. Knowing what is offshoring in supply chain management assists the companies to maximise production and increase global accessibility and efficiency of operations.
Offshoring Advantages
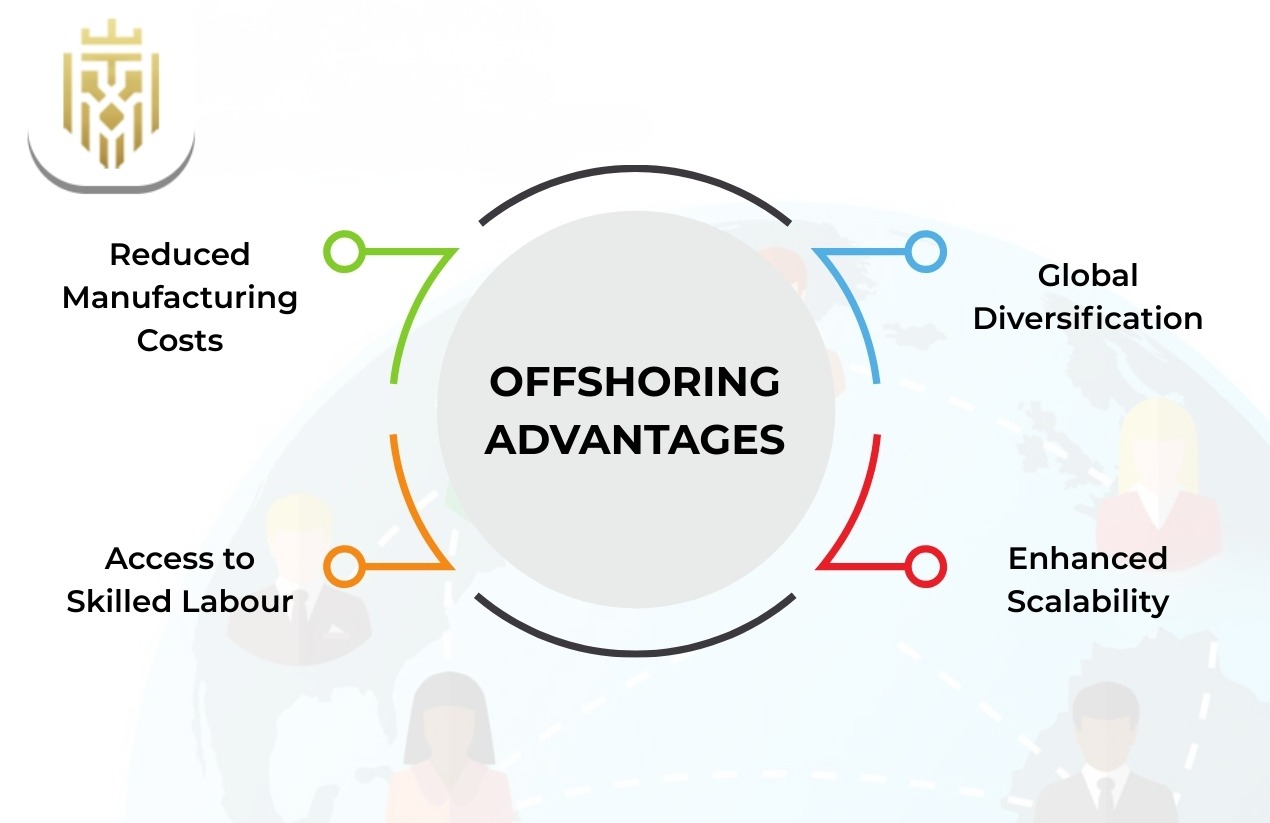
The major offshoring advantages are reduced manufacturing costs, access to skilled labour and better scalability. The benefits of offshoring support the global manufacturing strategy, as it allows companies to diversify the site of production. This model enhances competitive advantage, particularly for large businesses that rely on scalability in capacity and expanded market share through offshoring in supply chain structures.
Understanding Reshoring
Understanding what is reshoring is knowing that It is the process of returning the production and operations to the home country of the company. Onshore production is sought by businesses to increase the quality of products, control, and local manufacturing. Increasing focus on resilience and security reinforces reshoring supply chain approaches because companies are reallocating resources nearer to core markets.
Benefits of Reshoring
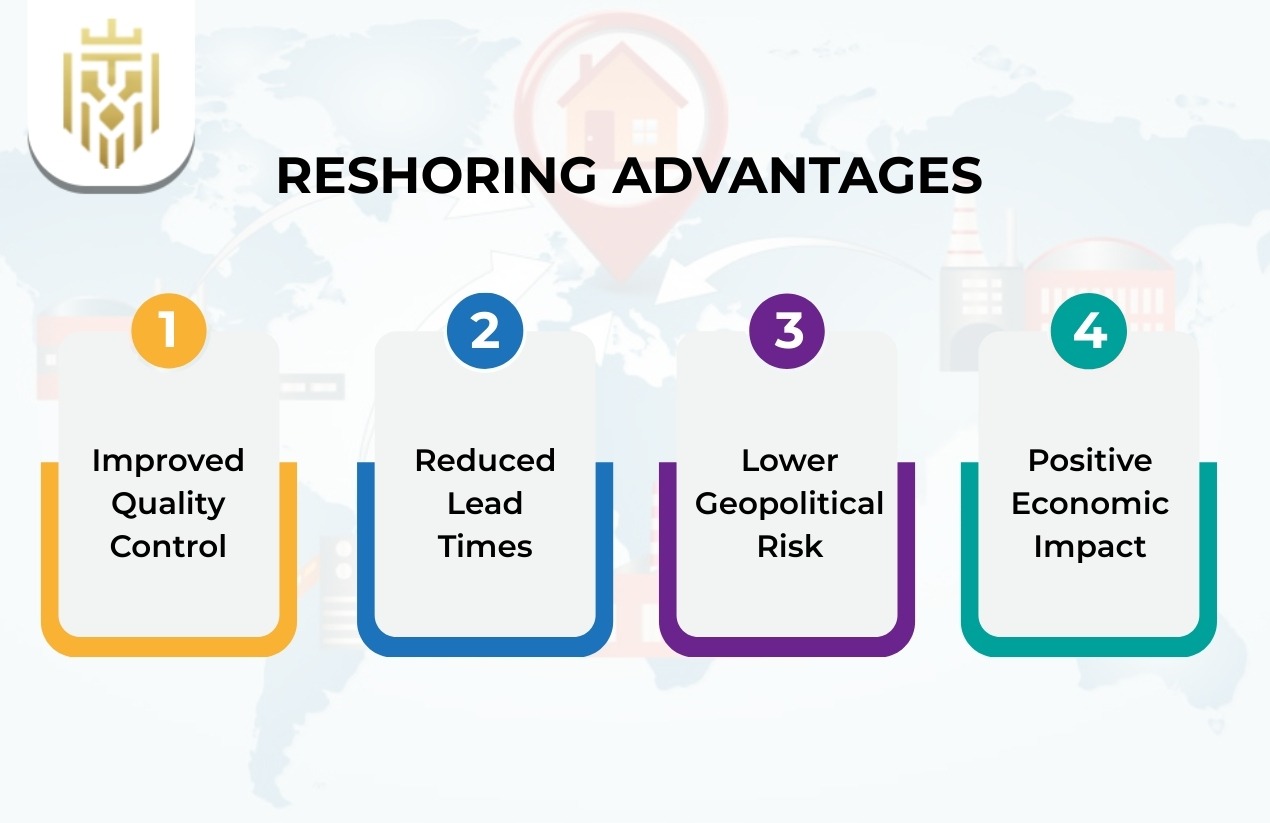
The benefits of reshoring are better quality control, reduced lead times and reduced geopolitical risk. Most companies emphasise the reshoring economic effect, including the creation of jobs and domestic production. With the increasing popularity of sustainability and regional resilience, the benefits of reshoring initiatives become increasingly popular among enterprises interested in long-term development and entering the market when it is stable.
Difference Between Offshoring & Reshoring
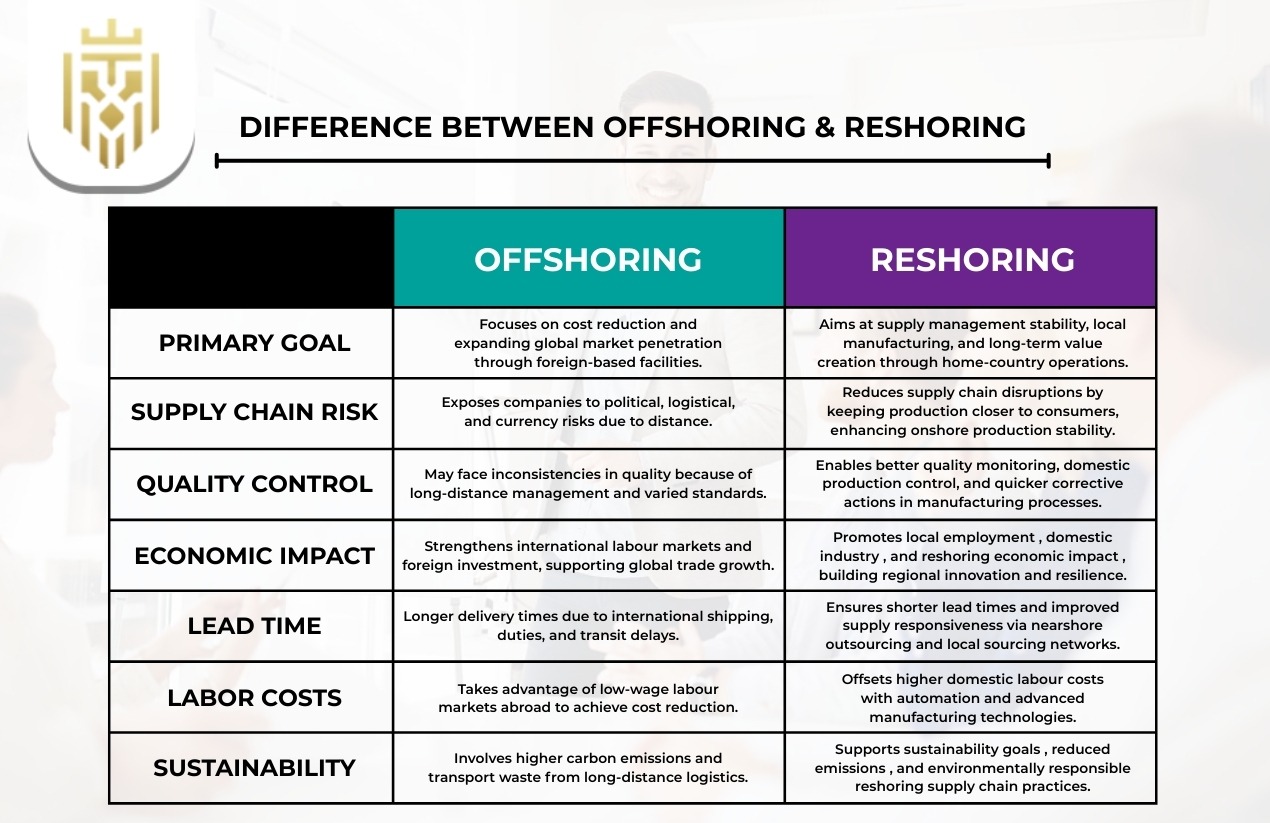
Offshoring vs reshoring are two opposite strategies of supply chain decision. Offshoring is concentrated on the efficiency of global trade, whereas reshoring enhances the local control and speed. Cost, risk, productivity, and workforce availability are the aspects that organisations consider when deciding on the direction to take in response to changing operational objectives and economic changes.
Primary Goal
The main difference between offshoring and reshoring is centred around cost reduction and global market penetration through the utilisation of foreign-based facilities, as opposed to the supply management stability and job creation in the home country. The local manufacturing flexibility and long-term value creation are some of the factors that companies adopting reshoring consider more than short-term savings.
Supply Chain Risk
Offshoring may put firms at risk of political, logistical and currency changes, and reshoring minimises supply chain risk by increasing the proximity of operations to consumers. Companies that use the onshore production method tend to register higher continuity of supply and reduced disruptions occasioned by international transportation and geopolitical strains.
Quality Control
Reshoring enhances monitoring and uniformity in quality using domestic production; the offshoring business process models could have quality differences owing to distance. The return to manufacturing will allow more efficient monitoring of the processes and provide timely corrective measures, and such a solution is attractive to the industries where accuracy is essential.
Economic Impact
Offshoring has positive effects on international labour markets and international investment, and reshoring encourages reshoring economic impact by increasing local manufacturing and local employment. Offshoring and reshoring both contribute to the development of the economies, but in different ways: the first strengthens international development, and the second one builds up the domestic industry and innovations.
Lead Time
Offshoring tends to add time to the transit and duties delay, but reshoring shortens delivery cycles by delivering onshore production. Enterprises planning to achieve better speed and responsiveness to customer demand are considering nearshore sourcing and local networks as a strategic agility tool.
Labour Costs
Offshoring uses cheaper wages in other countries as a cost reduction measure, whereas reshoring might entail the use of automation to balance higher labour costs in the domestic labour markets. In either seeking out labour markets in a global market or investing in high-tech manufacturing, companies consider the availability of labour, skills and overall operational worth.
Sustainability
The sustainability objectives are assisted in reshoring, which lowers the number of emissions and transport wastes compared to offshoring, which might need long-distance transportation. Global supply principles are increasingly becoming important to companies who, in their future-ready manufacturing decisions, are taking environmental performance and sustainability as key factors.
Economic and Strategic Implications
Decisions on offshoring and reshoring influence the global trade trends, investments in innovations, and labour growth. Firms can develop sustainable competitiveness by striking a balance between the global manufacturing approach and the resilience and ecological objectives to guarantee intelligent alignment of the cost, quality, and capacity planning strategic goals.
Manufacturing Costs and Competitiveness
Offshoring reduces the manufacturing costs and production costs in other countries, and reshoring increases the responsiveness to the market, and reshoring advantages include increased quality and agility. Organisations that embrace the hybrid approach, which is a combination of nearshore outsourcing and national presence, receive competitive pricing and reliability.
Impact on Global Trade and Economy
Offshoring expands the international trade networks and promotes global collaboration, whereas reshoring enhances the regional development and onshore production capacity. The trend of change of policies, automation, and demand shifts are all still going on to affect the supply flows across borders and the competitiveness in an international market.
Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility
The increasing ESG expectations compel companies to reconsider the offshoring vs. reshoring models. Numerous companies are focused on reducing emissions, sourcing ethically, and enhancing impact in the community by reinforcing the local presence. With the increasing compliance requirements, supply management practices are increasingly matching the sustainability commitment and responsible business practices.
FAQs
1) How does reshoring affect employment rates?
The common effects of reshoring are that it adds employment in the domestic country and boosts the local industries, manufacturing facilities and employment opportunities, particularly in a skilled and technical field.
2) What role does automation play in reshoring?
The automation reduces labour expenses, enhances production, and renders local production competitive, allowing organisations to reshore with efficiency and less dependence on the low-cost labour in foreign countries.
3) How does reshoring improve sustainability?
Reshoring not only lowers the emissions caused by long-distance transportation but also enhances the visibility of the supply chain and provides a chance to produce cleaner products, which can be used in the framework of environmental objectives and sustainable development.
4) Is nearshoring the same as reshoring?
No. Nearshoring brings the operations to the neighbouring countries, and reshoring brings the production back to the home country. Both reduce the supply chains but are of different locations.









