Supply Chain Management Definition
Supply Chain Management also known as SCM is the end-to-end coordination of all activities involved in sourcing, production, and delivery of products or services. It goes far beyond moving goods. It encircles everything from raw material procurement to demand forecasting, inventory handling, and post-sale service.
SCM incorporates suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers into a streamlined network that focuses on efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. It is a broad practice that needs balancing costs, time and resources while also managing risks such as supplier disruptions or demand fluctuations.
Modern supply chain management majorly depends on automation, intelligent vehicles, safety sensors, and smart navigation systems to enhance efficiency and resilience. While the terms are often used together as supply chain and logistics, it is essential to note that logistics is just one part of the wider supply chain.
Logistics Definition
Logistics is a specific part of the supply chain that focuses on the movement, storage, and handling of goods. It involves tasks such as warehousing, fleet management, inventory handling, distribution system and material transport.
Logistics is more tactical and operational, when supply chain management is broad and strategic. Logistics assures that goods get from one place to another on time, in the right condition, and at the lowest possible cost.
Technologies like automation in intralogitics, lean manufacturing practices, and industrial safety standards have transformed logistics into a precise and reliable function. Together, these methods shape what businesses often call the logistics and supply chain management definition, capturing how the two functions interconnect yet remain distinct.
Key Difference Between Logistics and Supply Chain Management
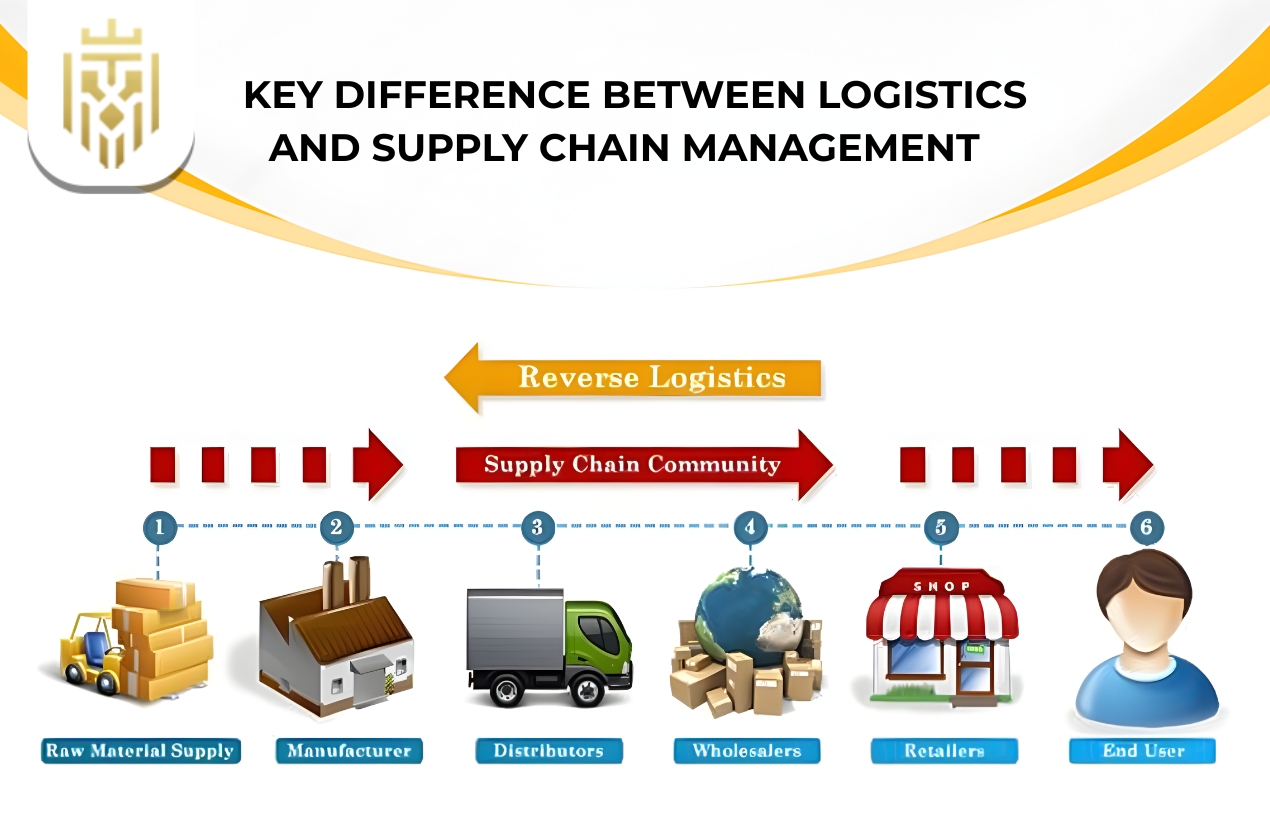
Though supply chain logistics are interlinked, they differ in scope, objectives, and strategic impact. Let’s explore these differences under key categories:
Scope of Operations
-
SCM encircles the entire value chain, including supplier relationships, demand planning, product development, manufacturing, logistics, and customer service. Supply Chain Management is more integral in nature.
-
Logistics deals primarily with transportation, storage, and distribution of goods. It has a confined operational scope focused on the movement and handling of inventory.
Objective
-
The objective of supply chain management is to create competitive advantage by enhancing efficiency, minimizing waste, and incorporating processes across all stakeholders.
-
The objective of logistics is to assure timely and cost-efficient delivery of goods with least risk and damage.
Timeframe of Impact
-
Supply Chain Management has a long term impact by shaping strategies that reduce costs, increase market share, and build customer loyalty.
-
Logistics impacts the short term by focusing on critical operational efficiency, like delivering an order to a customer.
Components Covered
-
Supply Chain Management encompasses procurement, supplier coordination, demand forecasting, manufacturing, quality control, logistics,and customer relations.
-
Logistics covers warehousing, transportation, inventory handling, fleet management, and distribution systems.
Process Orientation
-
SCM is strategy-driven, coordinating multiple processes to meet organizational goals.
-
Logistics is process-driven, prioritizing on repeatable tasks like routing shipments or managing storage.
Technology Usage
-
SCM uses advanced technologies such as blockchain for transparency, AI for demand prediction, and IoT for supply-chain efficiency.
-
Logistics uses tools like navigation systems, safety sensors, fleet monitoring, and warehouse automation.
Customer Focus
-
SCM goes deeper by analyzing customer demand patterns, that ensures product availability, and driving satisfaction through end-to-end coordination.
-
Logistics is customer-facing in the sense of operation that ensures on-time delivery and product safety.
Integration with Business Strategy
-
SCM is incorporated into corporate strategy, usually influencing product design, market expansion, and sustainability goals.
-
Logistics is supportive of business operations but not always directly tied to strategy.
Flow Management
-
Supply Chain Management manages forward, backward (returns), and information flow across the entire chain.
-
Logistics primarily handles the forward flow of goods
Decision-Making Levels
-
SCM decisions are strategic (e.g., where to set up a manufacturing plant).
-
Logistics decisions are operational (e.g., which carrier to use).
Role of Logistics in Supply Chain Management

Although logistics and supply chain management are different, logistics is an important part of SCM. It provides the execution layer that makes strategic supply chain decisions work in practice.
Movement of Goods
Logistics ensures effortless transportation of goods between suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and customers. This involves picking the right transport modes, roads, rail, air or sea, and optimizing routes with smart navigation tools. Modern logistics also accounts for sustainability by adopting fuel-efficient fleets and alternative energy.
Storage
Storage is another essential aspect of logistics. Efficient warehousing includes proper layout planning, automated picking systems, and real-time inventory tracking. The rise of intralogistics automation has enabled warehouses to reduce errors, improves safety standards, and improve productivity. Without proper logistics storage, even the best supply chain strategies can fail.
Future of Supply Chain and Logistics
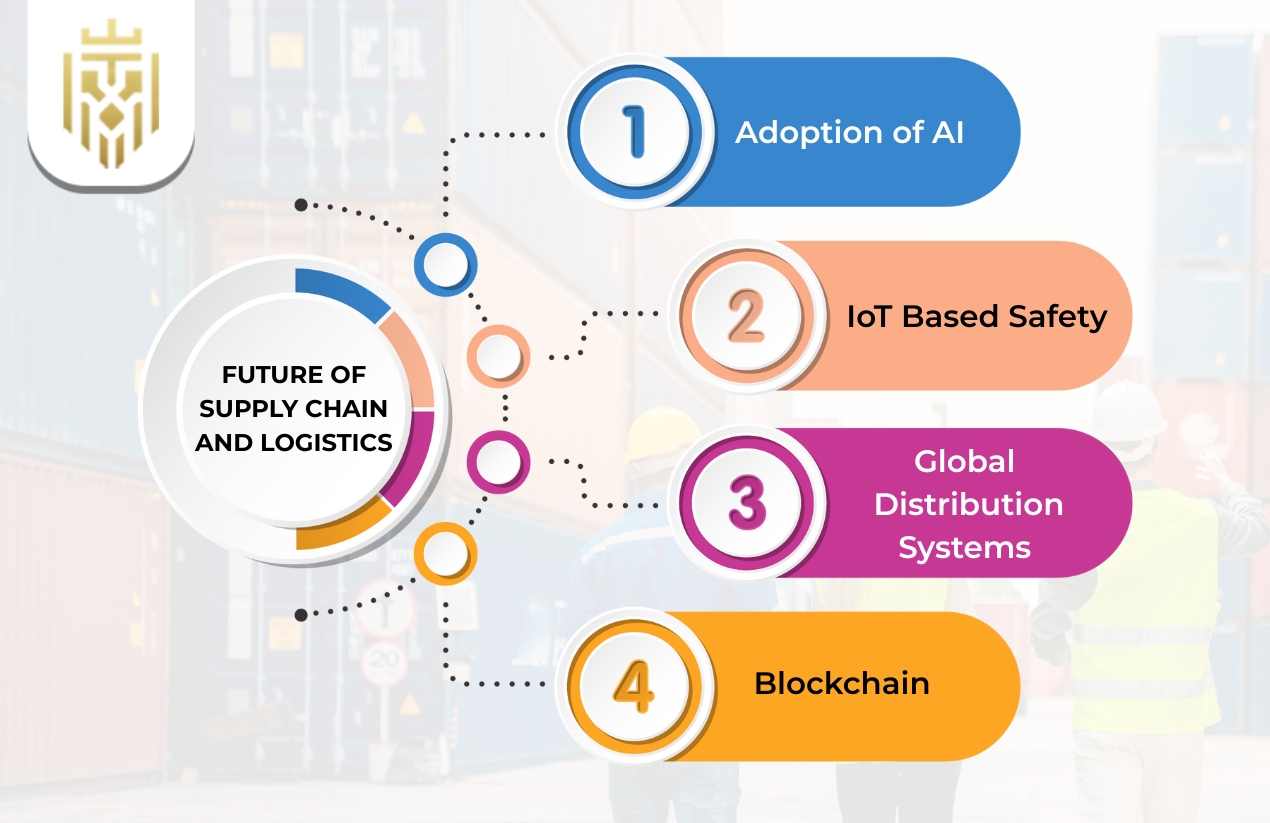
The future of supply chain and logistics is being formed by rapid technological advancements, global trade dynamics, and growing focus on sustainability.
Adoption of AI
Artificial Intelligence is converting both supply chain management and logistics. AI- driven demand forecasting, route optimization, and predictive maintenance of fleets help minimize costs while enhancing reliability. AI-powered chatbots and analytics tools also improve customer experience.
IoT Based Safety
The IoT (Internet of Things) is redefining safety in logistics and supply chain management. From sensors in warehouses that monitor temperature for short-lived goods to safety standards in fleets that track driver behavior, IoT assures reliability and compliance. IoT also contributes to industrial supply chain efficiency by providing real-time visibility across nodes.
Global Distribution Systems
As businesses extend globally, distribution systems are becoming more complex. Cloud-based platforms now grant organizations to coordinate multiple partners across regions effortlessly. Global distribution systems depend heavily on intelligent vehicles, intralogistics automation, and lean manufacturing processes to assures timely deliveries across borders.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology provides transparency, security, and accountability across the supply chain. It eliminates risks of fraud, assures compliance with safety standards, and builds trust among stakeholders. For logistics, blockchain improves visibility in material transport and distribution, making it easier to validate the authenticity of shipments.
FAQs
1) Is it possible for logistics to operate without supply chain management?
Not effectively. While logistics can function independently for tasks like delivery or warehousing, without supply chain management, it lacks coordination with sourcing, production, and demand planning. SCM ensures that logistics efforts are aligned with business goals.
2) Does inventory management belong to logistics or supply chain management?
Inventory management is a shared responsibility. Operationally, it is part of logistics because it involves warehousing and handling. Strategically, it belongs to SCM, as demand forecasting and procurement decisions influence stock levels.
3) What is the role of distribution systems in supply chain management success?
Distribution systems ensure that products reach the right customer at the right time. They connect production with demand, optimize costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Without efficient distribution, supply chain efficiency collapses.
4) What are the four types of logistics?
The four types are:
- Inbound logistics – moving raw materials from suppliers to manufacturers.
- Outbound logistics – delivering finished goods to customers.
- Reverse logistics – handling returns and recycling.
- Third-party logistics (3PL) – outsourcing logistics functions to specialized providers.









