What is Supply Chain Management Analytics?
Supply chain management analytics is the process of using data driven tools and techniques to monitor, optimize, and enhance supply chain operators. Unlike traditional approaches, analytics doesn’t just report what happened, but it also provides insights into why it happened and what is likely to occur next.
In supply chain management, predictive analytics stands out as a powerful part. it utilizes both historical and real time data to anticipate trends, like demand fluctuations, transportation delays, or risks. By leveraging data analytics in supply chain management, companies can shift from reactive strategies to proactive decision making.
Predictive Analytics in Supply Chain
Predictive analytics is all about foreseeing. In the context of the supply chain, it allows organizations to prepare for forthcoming challenges and opportunities. By incorporating large data sets from ERP systems, loT devices, customer feedback, and logistics networks, predictive models provide accurate forecasts.
This fore sighting approach provides assurance that businesses don’t just respond to issues after they occur but instead take precautionary measures to prevent them. Predictive analytics provide higher efficiency, reduced costs and stronger resilience.
Predictive Analytics Methods

Predictive analytics relies on a variety of methods, each serves to different aspects of the supply chain.
Predictive Modeling
Predictive Modeling is an approach that uses both historical and current data with machine learning to predict future events. It creates mathematical models that forecast outcomes based on data. For supply chain, Predictive modeling means anticipating lead times or predicting customer demand spikes. These models steadily improve, once the data is introduced.
Data Mining
Data mining involves extracting patterns from large, complex data sets. In data analytics in supply chain management, Data mining uncover hidden inefficiencies, supplier risks, or customer purchasing patterns that are not visible through manual analysis.
Time-series Forecasting
Time-series forecasting integrates historical data points to project future trends. In the supply chain, it is inestimable for demand forecasting and sales planning, helping businesses prepare for seasonal shifts or promotional events.
Simulation Models
Stimulation models copy the real world supply chain scenarios to test the consequences. For instance, a company may encourage the effect of a port closure or raw material shortage to understand the potential impact and mitigation strategies.
Regression & Classification Models
Regression models evaluates relationships between variables, such as how pricing impacts demand. Classification models assort data, like identify whether a suppleir poses a high or low risk. Both of the approaches strengthens predictive decision making.
Important Predictive Analytics Applications in Supply Chain
The most important impact of predictive analytics is seen in its practical applications across supply chain operations.
Demand Forecasting
Demand Forecasting refers to accurately predicting demand in the key element of supply chain success. Predictive analytics uses historical sales, market trends, and customer behavior to forecast demand levels. This decreases stock outs, reduces excess inventory, and aligns production with actual needs.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is one of the most essential predictive analytics applications in the supply chain. By examining past data and current trends, companies can upgrade stock levels, avoid overstocking, and improve cash flow.
Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial part of the supply chain and predictive Analytics. The supply chain faces risks that include natural disasters to geopolitical events. Predictive analytics identifies potential disruptions in advance, that allows businesses to expand supplier or reroute logistics to minimize impact.
Transportation & Logistics Management
Transportation & Logistics management is an integral part of supply chain and can impact businesses in a wide range. Transportation delays often disrupt the entire supply chain. Predictive analytics influence real-time tracking and traffic data to anticipate delays and recommend alternative routes, ensuring timely deliveries.
Production & Supply Planning
From raw material sourcing to production schedules, predictive analytics ensures supply planning aligns with demand. Manufacturers can improvise workforce allocation, machine usage, and resource distribution.
Advantages of Implementing Predictive Analytics
The advantages of predictive analytics in supply chain management extend far beyond forecasting. Predictive analytics enables supply chains to foresee demand, improve inventory, and minimize costs. By leveraging data driven insights, businesses can reduce risks, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Increased Visibility
Predictive analytics incorporates data from multiple sources, providing end-to-end clarity across supply chain. Businesses gain a fine understanding of where goods are, and how they are moving, and what issues can arise.
Data Driven Decision Making
With the use of insights from supply chain management analytics, decision are no longer based on guesswork. Leaders rely on data-backed predictions to make strategic choices, assuring alignment with business goals.
Stronger Resilience against Disruptions
Predictive analytics trains supply chain for uncertainty. Whether it’s a sudden rush in demand or logistics hurdles, companies can adjust quickly to maintain stability.
Lower Operational Costs
By upgrading inventory, transportation, and production, predictive analytics notably minimizes operational expenses. Cost savings directly translate into higher profitability and competitive advantage.
Best Practices for Predictive Supply Chain Analysis
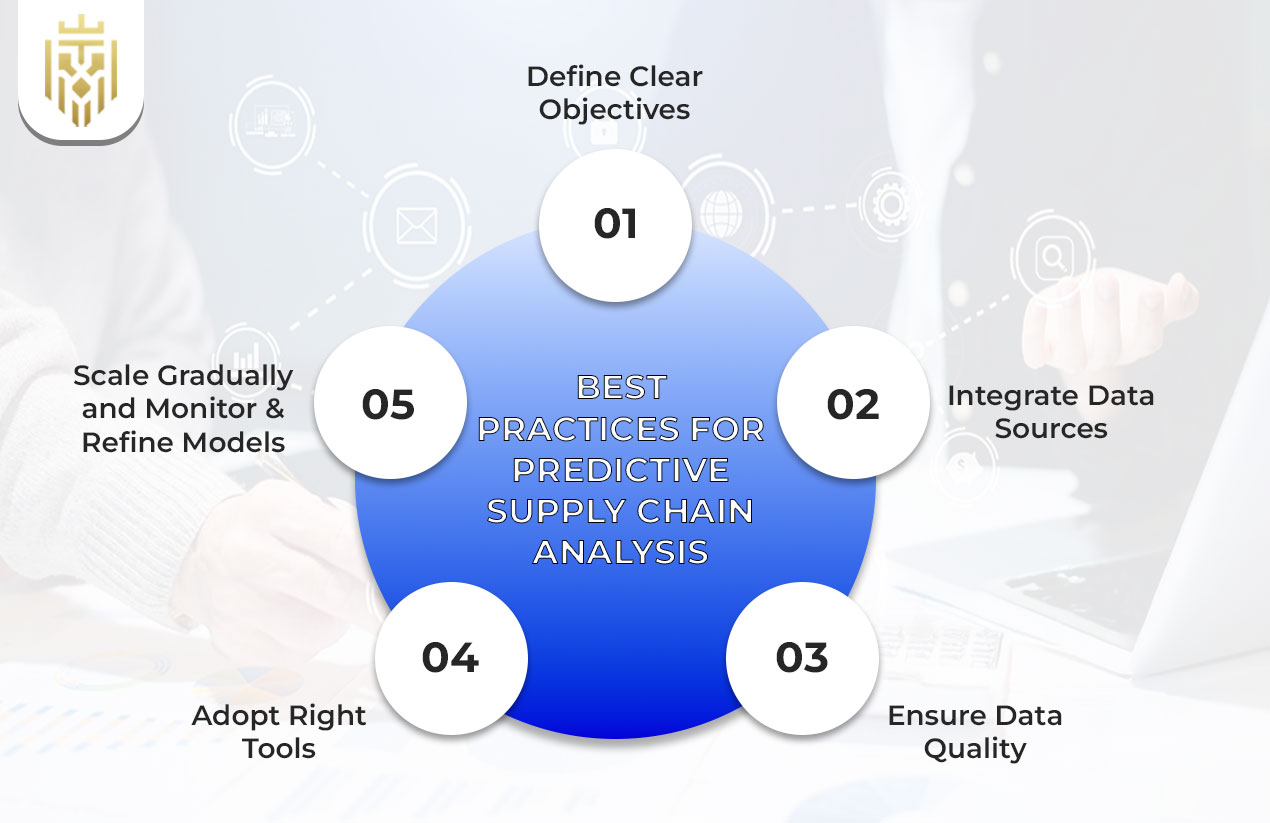
To adopt predictive analytics in businesses requires a structural and planned approach. Following are some best practices to adapt Predictive supply chain analysis.
Define Clear Objectives
Start with clear and defined objectives. Businesses must have specific goals, like improving forecast accuracy or reducing lead times. Having a clear objective ensures focused implementation.
Integrate Data Sources
Supply chain data comes from different sources such as, transport networks, warehouses, sales platforms, and loT devices. Integrating data sources ensures analytics models work with comprehensive and accurate information.
Ensure Data Quality
High-quality data is the heart of accurate predictions. Businesses must clean, validate, and make systematic data before feeding it into predictive models.
Adopt Right Tools
Choosing the correct analytics tools and platforms is essential. Cloud-based systems with machine learning capabilities provide extensible and advanced functionality.
Scale Gradually
Rather than overcrowding the entire supply chain, companies should start small, perhaps with demand forecasting, before scaling predictive analytics to other areas.
Monitor & Refine Models
Predictive models require frequent monitoring. Over time, businesses must refine them to reflect and adapt to new market dynamics, data sources, and customer behaviors.
FAQs
1) What role does real-time tracking data play in predictive forecasting?
Real-time tracking improves predictive forecasting by feeding live data into models. This enables dynamic adjustments in delivery schedules, route optimization, and improved customer satisfaction.
2) What data governance practices are critical for predictive supply chain analytics?
Strong and powerful governance assures data integrity, privacy, and compliance. Practices like data collection, access controls, and regular audits are crucial for reliable analytics.
3) How do cloud-based platforms support predictive analytics in logistics industry?
Cloud platforms provide scalability, flexibility, and access to advanced machine learning tools. They enable collaboration crosswise stakeholders and streamline the integration of diverse data sources.
4) How can predictive analytics enhance collaboration between suppliers and distributors?
By sharing predictive insights, suppliers and distributors align better on demand forecasts, inventory planning, and delivery schedules. This promotes stronger relationships and reduces miscommunication.









