What Is a Bill of Lading?
A bill of lading is a legal document that proves shipment between a shipper and a carrier. It serves a key role in global trade by ensuring goods are transported under clearly defined terms and responsibilities.
Why Does a Bill of Lading Matter?
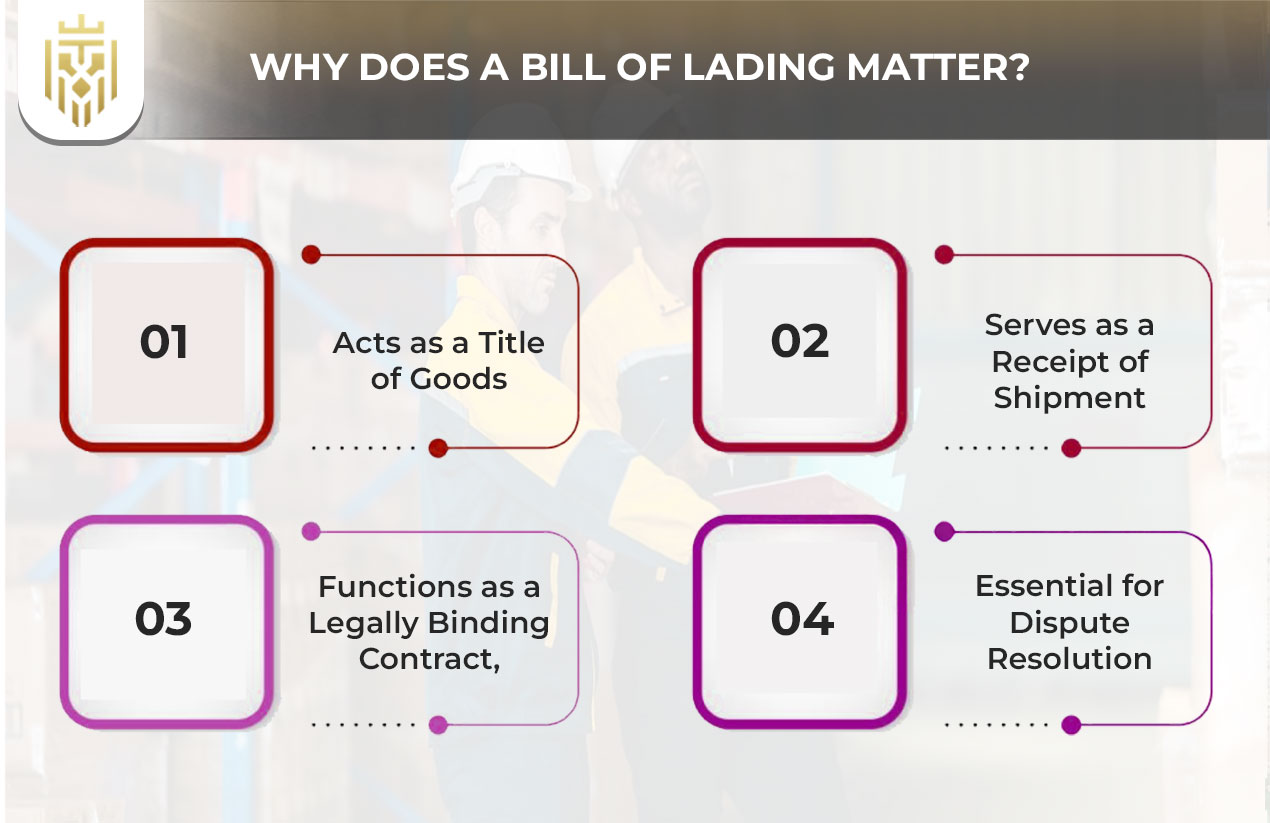
Understanding what a bill of lading is helps businesses avoid costly mistakes in international trade. It serves as a crucial record in disputes and ensures goods reach the correct destination through clear documentation and acknowledgement between parties like carriers and shippers.
Acts as a Title of Goods
The bill of lading often acts as a legal document that transfers the title of goods between buyers and sellers. This capability supports ownership rights throughout the logistics chain, providing security in international trade transactions and protecting the commercial interests of all parties.
Serves as a Receipt of Shipment
A bill of lading functions as a shipment receipt, confirming the carrier has received the goods in good condition. It is critical in international trade, where proof of shipment is needed before payments or customs clearances happen between countries.
Functions as a Legally Binding Contract
When issued, the bills of lading legally bind everyone involved. This document protects both the shipper and consignee by outlining responsibilities, liabilities, and freight terms. It is important for maintaining trust and compliance in global transactions and supply chains.
Essential for Dispute Resolution
A bill of lading serves as solid evidence in legal disputes related to delivery failures or damages. In international trade, this document helps courts or arbitrators quickly verify the agreed shipment terms, reducing lengthy legal battles and ensuring fairness in proceedings.
Types of Bills of Lading You Should Know
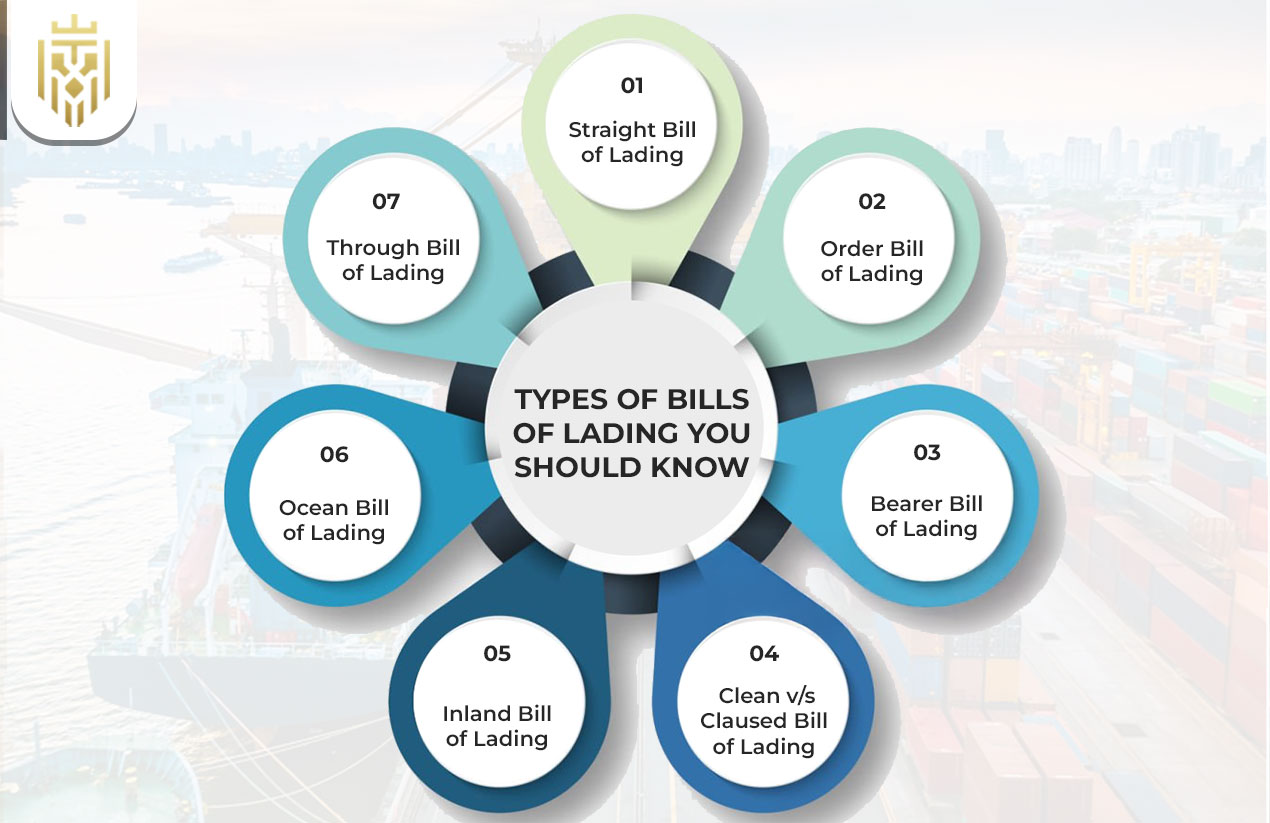
The different types of bills of lading serve unique purposes across logistics. Choosing the right type depends on factors like delivery conditions, destination, and the nature of the cargo. Using the wrong type can cause delays or legal issues in international trade.
Straight Bill of Lading
The straight bill of lading is non-negotiable and is delivered only to the named consignee. This prevents the transfer of goods to third parties during international trade, ensuring secure and transparent shipment processes to avoid fraud or mis delivery.
Order Bill of Lading
The order bill of lading is negotiable, allowing ownership transfer by endorsement. It plays an important role in securing transactions in international trade, where goods often change hands before reaching their final destination, providing flexibility and risk management through proper documentation.
Bearer Bill of Lading
The bearer bill of lading grants possession rights to whoever holds the document. This method allows for quick ownership transfers but requires caution in international trade to prevent unauthorised possession or fraudulent claims over goods in transit or storage.
Clean vs. Claused Bill of Lading
A clean bill of lading certifies that goods were received in perfect condition, while a claused one notes any discrepancies. Both are important in international trade negotiations, as buyers often need clean documents to secure financing or meet insurance requirements.
Inland Bill of Lading
The inland bill of lading covers domestic transportation before goods reach the ports for international trade. It is crucial for multi-modal logistics, connecting road or rail movement to maritime operations under a unified, compliant shipping arrangement.
Ocean Bill of Lading
An ocean bill of lading is essential in global shipping. It outlines specific maritime terms and ensures the carrier is accountable from port to port. Such documents protect all stakeholders’ interests throughout international trade routes and transactions.
Through Bill of Lading
The through bill of lading streamlines multi-leg shipments involving different modes of transport. It simplifies documentation in international trade and ensures cargo transitions smoothly between carriers while maintaining clarity on obligations, responsibilities, and ownership rights during transit.
Key Components in a Bill of Lading

Key components include shipper and consignee information, carrier name and transport mode, description of goods, origin and destination points, packaging details, freight terms and charges, and date of shipment and signatures. These elements ensure the bill of lading functions properly as a legal document for smooth operations in international trade.
Shipper and Consignee Information
Details about the shipper and consignee are vital for clarity in a bill of lading. Correct identification prevents confusion during international trade processes, ensuring accurate delivery and compliance with regulations across borders.
Carrier Name and Transport Mode
Carrier names and selected transport modes are clearly stated in a bill of lading. These details clarify responsibilities, support logistics planning, and reduce disputes in international trade by confirming shipping arrangements through recognised industry standards.
Description of Goods
The goods’ detailed description in a bill of lading helps customs authorities and shipping companies. Accurate documentation prevents misunderstandings in international trade and ensures compliance with relevant import-export regulations for smooth transit and timely delivery.
Origin and Destination Points
Clear origin and destination details are mandatory in any bill of lading. These points help streamline logistics and customs clearance during international trade, ensuring cargo reaches its intended recipient through clear, trackable routes and verified shipping instructions.
Packaging Details
Clear packaging descriptions lower the risk of damage or disputes. A bill of lading should specify whether goods are crated, palletised, or containerised, ensuring carriers understand how to handle cargo throughout various stages of international trade logistics.
Freight Terms and Charges
Freight terms and charges clarify payment responsibilities between shippers and consignees. Including these in a bill of lading protects parties during international trade and minimises disagreements by establishing expectations on costs, duties, and liabilities upfront.
Date of Shipment and Signatures
Accurate shipment dates and authorised signatures validate the bill of lading. This information is essential for audits of international trade documentation and prevents legal disputes, proving that contractual obligations were met within the agreed timeframe.
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them

Avoid errors like mismatched shipping details, incorrect classification of goods, missing signatures or stamps, use of expired or invalid templates, failure to update terms of delivery, and typographical or clerical errors. These issues can lead to disputes and delays, impacting delivery accuracy and credibility in international trade logistics.
Mismatched Shipping Details
Mismatched details in a bill of lading can cause customs delays or rejections. To protect international trade transactions, check that all information matches booking confirmations, invoices, and other documentation before issuing the final shipping paperwork.
Incorrect Classification of Goods
Incorrectly classified goods on bills of lading may result in penalties or delays. Knowing proper classification protocols within international trade helps prevent costly mistakes and ensures compliance with customs regulations in both origin and destination countries.
Missing Signatures or Stamps
Missing signatures invalidate a bill of lading, making it unusable in international trade. Ensure all required parties, including the shipper, carrier, and consignee, authorise the document properly to avoid legal or operational complications later.
Use of Expired or Invalid Templates
Expired or outdated templates can compromise the accuracy of bills of lading. Using current formats recognised in international trade protects companies from rejections or compliance issues, ensuring smooth processing through customs and related authorities.
Failure to Update Terms of Delivery
Failing to update delivery terms can lead to confusion in a bill of lading. In international trade, make sure all terms reflect the most recent agreement to prevent legal challenges or disputes regarding payment, responsibilities, or delivery expectations.
Typographical or Clerical Errors
Clerical mistakes in a bill of lading can cause significant delays in international trade. Careful proofreading before finalising documents reduces risks and ensures shipments proceed smoothly without unnecessary administrative obstacles or rejections.
Best Practices for Managing Bills of Lading
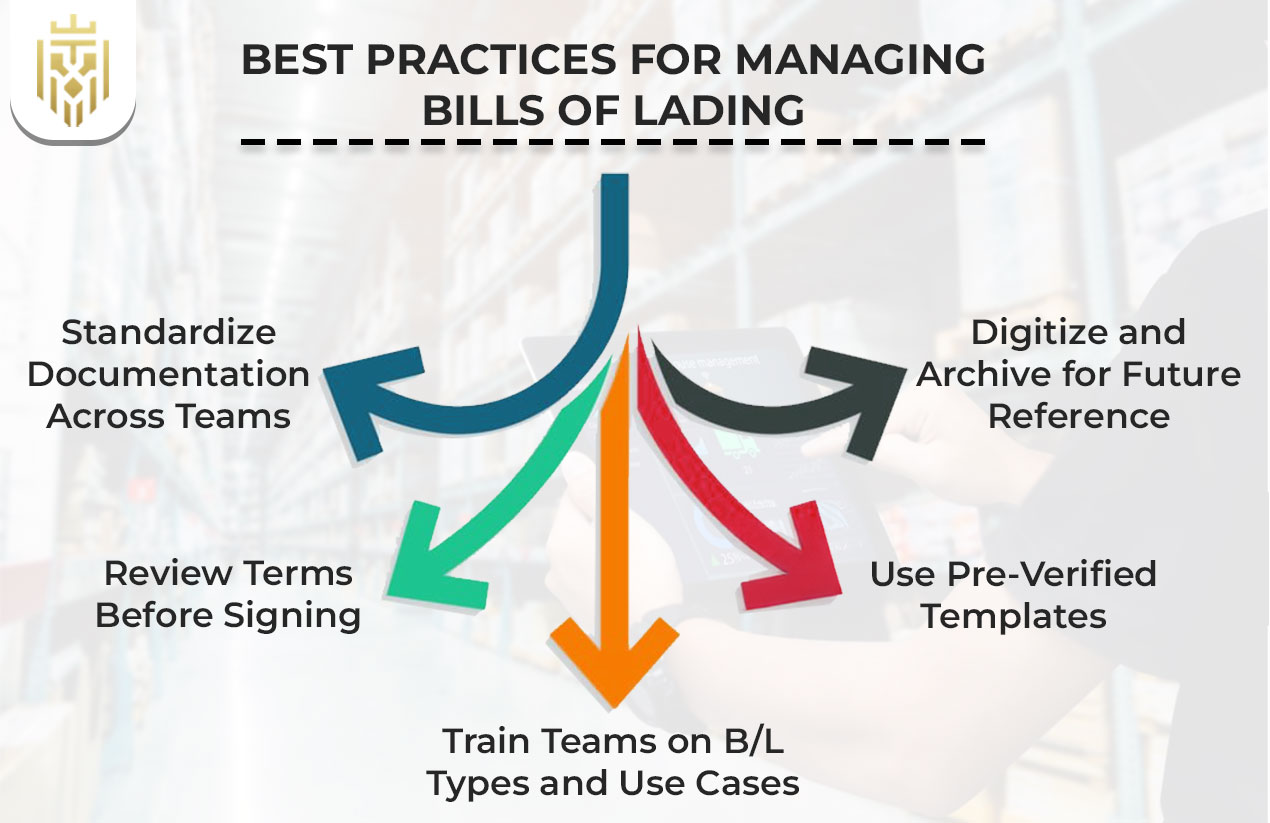
Standardise documentation across teams, review terms before signing, and train teams on bill of lading types and uses. These best practices improve accuracy, protect legal interests, and strengthen bill of lading management in international trade.
Standardise Documentation Across Teams
Standardising bill of lading processes across departments boosts accuracy and efficiency. It helps businesses avoid inconsistencies and builds reliability, especially in complex international trade settings where precise documentation is crucial for compliance.
Review Terms Before Signing
Carefully reviewing terms helps prevent disputes over a bill of lading. Clarify responsibilities, liabilities, and delivery expectations before approval. This diligence benefits everyone involved, streamlining international trade transactions and fostering positive business relationships through transparency.
Train Teams on B/L Types and Use Cases
Training teams on different types of bills of lading minimises errors and improves compliance. Employees gain clarity on specific use cases, reducing risk and enhancing efficiency within international trade supply chains and shipping operations.
Use Pre-Verified Templates
Using pre-verified templates ensures consistency and accuracy when issuing bills of lading. These templates reflect best practices aligned with international trade requirements, minimising errors and maintaining high documentation standards across various industries and logistics networks.
Digitise and Archive for Future Reference
Digitising and archiving bills of lading simplifies access and enhances security. This approach supports audit readiness and streamlines processes in international trade, making retrieval and compliance reporting more efficient for future business needs.
Role of Freight Forwarders and Carriers
Freight forwarders and carriers handle draughting and issuing bills of lading, coordinating with ports and customs, and ensuring legal compliance. Their role clarifies who issues bills of lading and strengthens documentation reliability for global international trade operations.
Draughting and Issuing B/Ls
Freight forwarders usually take care of draughting and issuing the bill of lading. If you’re curious about who issues bills of lading, it’s often these professionals who ensure accuracy for smooth international trade while aligning documentation with legal and contractual standards.
Coordinating with Ports and Customs
Freight forwarders work with ports and customs to ensure bills of lading meet regulatory standards. Their role is critical in expediting shipments through international trade hubs and reducing delays caused by incomplete or non-compliant documentation.
Ensuring Legal Compliance
Freight forwarders and carriers uphold legal document standards when issuing bills of lading. They make sure documents comply with international trade regulations, lowering risks tied to inaccuracies and protecting all stakeholders through compliant processes.
Supporting Claim Settlements
A bill of lading supports efficient claim settlements when disputes arise. In international trade, this document serves as verifiable proof, helping insurers, carriers, and shippers resolve issues quickly, ensuring accountability, and protecting commercial interests.
Digital Transformation in Bill of Lading
Recent developments include electronic bill of lading (eB/L) adoption, blockchain-based bills of lading for transparency, and smart contracts for automatic verification. These innovations streamline bill of lading processes and secure data integrity in fast-moving international trade environments.
Electronic Bill of Lading (eB/L) Adoption
The rise of electronic bill of lading adoption simplifies processes while enhancing security and efficiency in international trade. eB/L reduces paperwork and speeds up documentation flow, benefiting all stakeholders through faster verifications and easier handling.
Blockchain-Based B/L for Transparency
Blockchain-based bills of lading enhance transparency by securing records on decentralised ledgers. This innovation strengthens the integrity of international trade, ensuring documents are tamper-proof and traceable throughout the shipment journey, from origin to final delivery.
Smart Contracts for Auto-Verification
Smart contracts automate verification processes within blockchain-based bills of lading. These contracts ensure compliance and trigger actions when conditions are met, improving security and operational efficiency in international trade while reducing manual intervention.
Real-Time Tracking Integration
Integrating real-time tracking with bills of lading boosts visibility for shippers and consignees. In international trade, this feature supports proactive decision-making, minimises disruptions, and enhances customer satisfaction through transparent logistics and shipment updates.
FAQs
1) What is the purpose of a bill of lading in shipping?
It acts as a receipt, contract, and title for goods. This ensures clarity in shipping terms and responsibilities among the shipper, carrier, and receiver.
2) Can a bill of lading be issued electronically?
Yes, electronic versions known as eB/Ls are widely used. They offer faster processing, better security, and greater efficiency in managing shipping documents across global trade networks.
3) What is the difference between a bill of lading and an invoice?
A bill of lading is a shipping document that confirms receipt and terms, while an invoice details payment terms, item costs, and financial obligations between the buyer and seller.
4) Who issues the bill of lading?
The carrier or freight forwarder usually issues the bill of lading after goods are received. This document confirms the shipment details, responsibilities, and agreed transport terms among all parties involved.
5) What happens if there’s a mistake in the bill of lading?
Mistakes can delay shipments, cause legal disputes, or create customs problems. Corrections must be made quickly to ensure accuracy and avoid issues in shipping or delivery.
6) Is a bill of lading required for all international shipments?
Yes, it is generally required for most international trade shipments. This ensures proper documentation, legal proof of shipment, and compliance with customs regulations and transportation agreements.
7) What does a clean bill of lading mean?
A clean bill of lading confirms that goods were received in good condition, without visible damage or discrepancies. This supports smooth delivery and reduces the risk of disputes later.
8) Can a bill of lading be transferred to another party?
Yes, depending on its type, it can be transferred through endorsement. This allows another party to claim the goods, especially in transactions involving trade finance or resale.